OpenSwitch allows you to create one or more logical groups of servers (each group containing any number of Adaptive Servers), and to route individual connections to a given pool of servers using the incoming user name, the host name, or the application name of the connection as illustrated in Figure 1-3. This ensures that administrative requests or automatic failover occurs at the same time and in the same way for all application users.
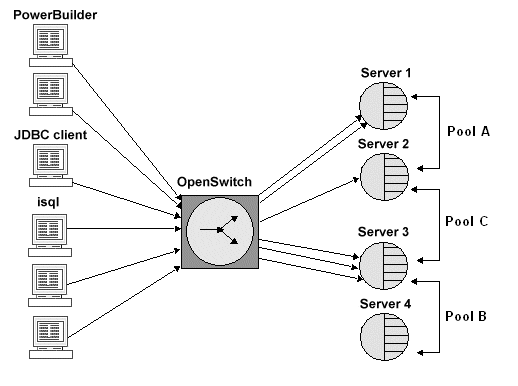
In this example, all incoming PowerBuilder® connections are routed to Pool A, for which the primary server is Server 1 and the failover server is Server 2. The JDBC client connections are routed to Pool C, for which the primary server is Server 2 and the failover server is Server 3. All isql connections are routed to Pool B, for which the primary server is Server 3 and the failover server is Server 4.
See “Defining pools” for more information about using server pools and routing.