A database can serve as an input to or output from a replication process or a transformation process. The structure of the database is modeled in one or more Physical Data Models (PDM) that can, in turn, be linked to a live database.
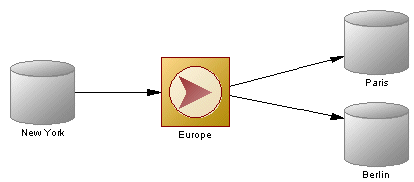
In the following example, data from the New York source database is replicated by the Europe replication process (see Replication Processes (DMM)) to the Paris and Berlin remote databases:
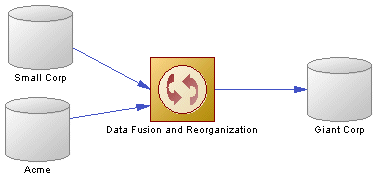
In the following example, data from the Small Corp and Acme databases is transformed by the Data Fusion and Reorganization transformation process (see Transformation Processes (DMM)), and loaded to the Giant Corp data warehouse:
You can generate to or reverse-engineer from your live database using the commands available from the database contextual menu (see Database Contextual Menu).