Figure 3-7 illustrates a warm standby application for a replicate database. In this example, a single Replication Server manages three databases:
A primary database,
The active database for a logical replicate database, and
The standby database for a logical replicate database.
The logical replicate database has subscriptions for the data in the primary database. Therefore, updates from the primary database are replicated to both the active and the standby databases.
In this example, a single Replication Server manages both the primary and replicate databases. In other instances, different Replication Servers may manage the primary and replicate databases.
Figure 3-7: Warm standby application for a replicate database
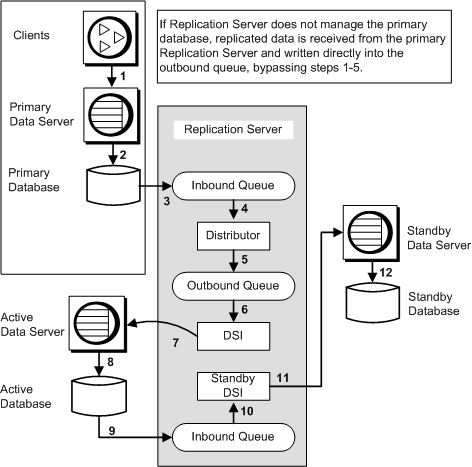
The numbers in Figure 3-7 indicate the flow of transactions from client applications through the replication system in a warm standby application for a replicate database.
In Figure 3-7, numbers 1 through 8 trace transactions from clients to the primary database, and, via normal replication, to the active replicate database:
Clients execute transactions in the primary data server.
The primary data server updates the primary database.
RepAgent for the primary database reads transactions for replicated data in the transaction log and forwards them to the Replication Server, which writes them into an inbound queue.
The Distributor thread reads transactions from the inbound queue.
The Distributor processes transactions against subscriptions and writes replicated transactions into an outbound queue.
If the Replication Server managing the warm standby application for the replicate database does not also manage the primary database, replicated data is received from the primary Replication Server and written directly to the outbound queue. Steps 1 through 5 are bypassed.
A DSI thread reads transactions from the outbound queue.
The DSI thread executes the transactions in the replicate data server, which is the active data server for the warm standby application.
The active data server updates the active database.
If the transactions originate in a primary database managed by a different Replication Server, the Distributor thread in the primary Replication Server writes them into an RSI outbound queue. Then they are replicated to a DSI outbound queue in the replicate Replication Server in order to be applied in the active database for the logical replicate database.
In Figure 3-7, numbers 9 through 12 trace transactions from the active database for the logical replicate database to its standby database:
RepAgent for the active database reads the transactions in the active database log and forwards them to the Replication Server, which writes them into an inbound queue.
All transactions for replicated data, including those executed by the maintenance user, are sent to the Replication Server for application in the standby database.
The standby DSI thread reads transactions from the inbound queue.
The standby DSI thread executes transactions in the standby data server.
The standby data server updates the standby database.