Summary information |
|
|---|---|
Default value |
512 |
Range of values |
512–65024 |
Status |
Static |
Display level |
Intermediate |
Required role |
System administrator |
Configuration group |
Network Communication |
max network packet size specifies the maximum network packet size that can be requested by clients communicating with Adaptive Server.
If some of your applications send or receive large amounts of data across the network, these applications can achieve significant performance improvement by using larger packet sizes. Two examples are large bulk copy operations and applications that read or write large text, unitext, and image values.
Generally, you want:
default network packet size to be small for users who perform short queries, and
max network packet size to be large enough to allow users who send or receive large volumes of data to request larger packet sizes.
max network packet size must always be as large as, or larger than, the default network packet size. Values that are not even multiples of 512 are rounded down.
For client applications that explicitly request a larger network packet size to receive, you must also configure additional network memory. See “additional network memory”.
Open Client Server cannot accept a network packet size greater than 64K.
See bcp and isql in the Utility Guide for information on using larger packet sizes from these programs. Open Client Client-Library documentation includes information on using variable packet sizes.
For best performance, choose a server packet size that works efficiently with the underlying packet size on your network. The goals are:
Reducing the number of server reads and writes to the network
Reducing unused space in network packets (increasing network throughput)
For example, if your network packet size carries 1500 bytes of data, setting the Adaptive Server packet size to 1024 (512*2) will probably achieve better performance than setting it to 1536 (512*3). Figure 5-3 shows how four different packet size configurations would perform in such a scenario.
Figure 5-3: Factors in determining packet size
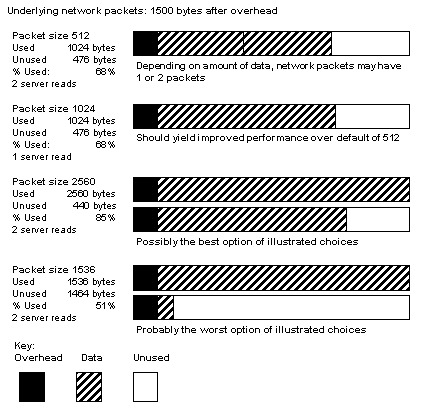
After you determine the available data space of the underlying packets on your network, perform your own benchmark tests to determine the optimum size for your configuration.
Use sp_sysmon to see how changing max network packet size affects network I/O management and task switching. For example, try increasing max network packet size and then checking sp_sysmon output to see how this affects bcp for large batches. See the Performance and Tuning Series: Monitoring Adaptive Server with sp_sysmon.