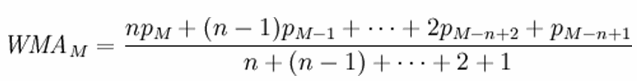Calculates an arithmetically (or linearly) weighted average.
A weighted average is an average in which each quantity to be averaged is assigned a weight. Weightings determine the relative importance of each quantity that make up the average.
Parameters
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
expression |
A numeric expression for which a weighted value is being computed. |
Usage
Use the WEIGHTED_AVG function to create a weighted moving average. In a weighted moving average, weights decrease arithmetically over time. Weights decrease from the highest weight for the most recent data points, down to zero.
To exaggerate the weighting, you can average two or more weighted moving averages together, or use an EXP_WEIGHTED_AVG function instead.
You can specify elements of window-spec either in the function syntax (inline), or with a WINDOW clause in the SELECT statement.
window-spec:
Must contain an ORDER BY specifier.
Cannot contain FOLLOWING or RANGE specifiers.
The second argument of the ROW specifier—if provided—must be CURRENT ROW.
Cannot contain NULL values.
Cannot contain the DISTINCT specifier.
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING is supported, but may result in poor performance if used
Example
SELECT DepartmentID, Surname, Salary,
WEIGHTED_AVG(Salary) OVER (PARTITION BY DepartmentID
ORDER BY YEAR(StartDate) DESC) as "W_AVG"
FROM Employees
WHERE State IN ('FL') ORDER BY DepartmentID
The returned result set is:
DepartmentID |
Surname |
Salary |
W_AVG |
|---|---|---|---|
100 |
Lull |
87,900.000 |
87,900.000000 |
100 |
Gowda |
59,840.000 |
69,193.333333 |
200 |
Sterling |
64,900.000 |
64,900.000000 |
200 |
Kelly |
87,500.000 |
79,966.666667 |
300 |
Litton |
58,930.000 |
58,930.000000 |
400 |
Evans |
68,940.000 |
68,940.000000 |
400 |
Charlton |
28,300.000 |
41,846.666667 |
400 |
Francis |
53,870.000 |
47,858.333333 |