For best performance, choose a server packet size that works efficiently with the underlying packet size on your network.
-
Reducing the number of server reads and writes to the network
-
Reducing unused space in network packets (increasing network throughput)
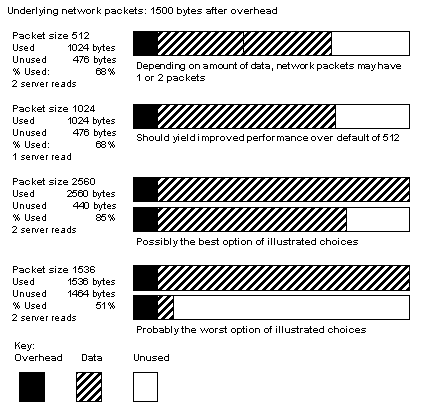
For example, if your network packet size carries 1500 bytes of data, setting the SAP ASE packet size to 1024 (512*2) will probably achieve better performance than setting it to 1536 (512*3). The figure below shows how four different packet size configurations would perform in such a scenario.
After you determine the available data space of the underlying packets on your network, perform your own benchmark tests to determine the optimum size for your configuration.
Use sp_sysmon to see how changing max network packet size affects network I/O management and task switching. For example, try increasing max network packet size and then checking sp_sysmon output to see how this affects bcp for large batches. See the Performance and Tuning Series: Monitoring SAP Adaptive Server with sp_sysmon.