

DirectConnect processing can involve CT-Library, DB-Library, and ODBC. The following figure shows DirectConnect processing with DB-Library (for more information, see the Mainframe Connect DirectConnect for z/OS Option User's Guide for DB2 Access Services):
Figure 8-3: Client-to-DirectConnect-to-mainframe processing
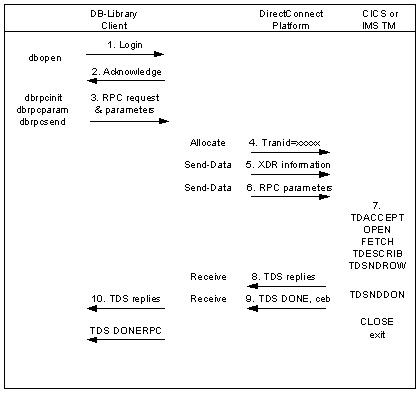
The following points describe the sequence shown in Figure 8-3 and highlight Enterprise Connect requirements:
![]() The following points describe both RPC and dynamic SQL
process flows.
The following points describe both RPC and dynamic SQL
process flows.
Assuming DirectConnect is started, the client opens a LAN connection to a designated DirectConnect Service and logs in. If the following message occurs:
Server name not found in interface file
make sure:
The client interfaces file is correctly set up.
The client Sybase path variable is correctly defined.
The DirectConnect server is specified in the DSQUERY variable.
For TRS only – On receiving the client login information, DirectConnect checks security as follows:
If security is turned on, DirectConnect ensures the client is authorized. If the client is not authorized, the following error occurs:
Security Violation: Login denied (no login entry).
If the client is authorized or security is turned off, DirectConnect acknowledges the login.
When the client application needs to invoke an RPC or language request on the mainframe, the client sends a request to DirectConnect over the LAN connection.
DirectConnect receives the request and searches the lookup table to find the mainframe session and the Server Option transaction ID to use. Entries for the RPC and connection must occur in the table. If security is turned on, the client must have authorization to use the RPC and connection to the mainframe. If the lookup table search and security check are successful, the line is up, and the session is active, DirectConnect allocates a conversation with the named transaction.
If a failure occurs during this process, one of the following error messages is written to both the DirectConnect log and client.
If the client is not authorized or is not listed correctly, the following error message occurs:
Security Violation: Access to RPC ‘xxxx’ denied.
If connections to the mainframe are unavailable, the following error message occurs:
Request Rejected: No host connections are available.
If an RPC name was entered incorrectly, or if the RPC name does not occur in the lookup table, the following message occurs:
Request Rejected: Remote procedure ‘xxxx’ not found.
DirectConnect sends the client’s External Data Representation (XDR) information and RPC parameters to the mainframe and waits for a reply from the transaction.
On the mainframe, the transaction processor initiates the named transaction, and the transaction issues the Server Option Gateway-Library calls. These calls read the client’s XDR information and RPC parameters. The transaction also performs associated processing, such as the issuing of static SQL DB2 requests or reading VSAM or other database data.
The transaction issues Gateway-Library calls to send results back to the client. These calls perform any data conversions, generate the TDS reply datastream, and send out reply data.
DirectConnect receives each TDS reply packet and forwards it to the client, which continues until the Server Option transaction issues a TDSNDDON call.
If a failure occurs during this process, an error message is written to the DirectConnect log. An “Unexpected EOF from Adaptive Server” message is written to the client. (The mainframe is acting as an Adaptive Server.)
Gateway-Library tracing functions, if in use, also record errors in this process. See Figure 8-2.
When finished with the request, the transaction exits, and the conversation terminates. For a long-running transaction (also called a user-defined transaction), the transaction can remain active through multiple requests before the conversation terminates. If a long-running transaction ends before it finishes processing, you should determine whether the appropriate client support is set up:
The client can be set up to disconnect after invoking the transaction and before the transaction ends.
Adaptive Server may log out after sending a client request, making long-running transactions impossible.
![]() AMD2 supports user-defined transactions,
which are comparable to long-running transactions based on Gateway-Library
support.
AMD2 supports user-defined transactions,
which are comparable to long-running transactions based on Gateway-Library
support.
| Copyright © 2005. Sybase Inc. All rights reserved. |

|
|