Figure 1-1 illustrates the basic components in a typical Sybase replication system.
Figure 1-1: Typical Sybase replication system
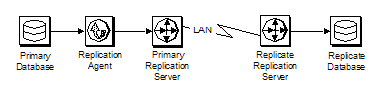
The following sections describe the primary-side components of a typical Sybase replication system:
Primary databases
Replication Agents
Replication Servers
A primary database is the source of transactions that modify data in the replicate databases. Transactions are replicated by table or by procedure.
Tables marked for replication in a primary database are called primary tables. A primary table must be marked for replication so that the Replication Agent can identify and replicate the transactions that affect the data in that table.
Large-object (LOB) columns within a primary table must have replication enabled separately from the primary table. You can selectively replicate LOB columns within a primary table.
To replicate invocations of a stored procedure, the procedure must be marked for replication so that the Replication Agent can identify and replicate invocations of that procedure in the primary database.
A Replication Agent is the Sybase replication system component that captures the replicated transactions in a primary database, and then sends those transactions to a Replication Server for distribution to replicate databases.
Sybase Replication Agent reads a transaction log in the primary database and generates Log Transfer Language (LTL) output. LTL is the language that Replication Server uses to process and distribute replicated transactions throughout a replication system.
Sybase Replication Agent can be configured to use information stored in the Replication Server System Database (RSSD) of the primary Replication Server to provide more sophisticated replication features and generate more efficient LTL.
There are two types of Sybase Replication Agents:
Trigger-based
Log-based
Trigger-based Replication Agents use triggers on marked tables to capture the data involved in a replicated transaction. The triggers also record other information the Replication Agent needs to replicate the transaction, such as a transaction ID that identifies each operation associated with a transaction.
Stored procedure replication is accomplished by similar triggers embedded in the stored procedure code.
When fired, the triggers record the data (or procedure invocation) to be replicated in one or more transaction log tables in the primary database. The transaction log tables are user tables created and maintained by the Replication Agent.
The Replication Agent creates the data-capture triggers in the primary database when a table or stored procedure is marked for replication. The triggers are removed by the Replication Agent when the table or procedure is unmarked.
Sybase Replication Agent uses the trigger-based solution for the Microsoft SQL Server primary database.
Log-based Replication Agents retrieve the information they need for transaction replication from the native transaction log maintained by the primary data server.
Sybase Replication Agent uses the log-based solution for primary databases in following primary databases:
DB2 Universal Database
Oracle
![]() Procedure and DDL replication is not available for DB2
Universal Database.
Procedure and DDL replication is not available for DB2
Universal Database.
The Replication Server that receives replicated transactions from a primary database (that is, directly from a Replication Agent) is called the primary Replication Server. The Replication Server that sends replicated transactions to a replicate database is called the replicate Replication Server.
![]() In a simple replication system, a single Replication
Server can act as both the primary Replication Server and the replicate
Replication Server.
In a simple replication system, a single Replication
Server can act as both the primary Replication Server and the replicate
Replication Server.
After it receives LTL from a Replication Agent, the primary Replication Server sends the replicated transaction to a replicate database, either directly or through a replicate Replication Server. The replicate Replication Server converts the replicated transaction from the LTL it receives to the native language of the replicate database, and then it sends the replicated transaction to the replicate data server for processing. When the replicated transaction is processed successfully by the replicate database, the replicate database is synchronized with the primary database.
Each Replication Server holds transaction operations in a stable queue and delivers them as soon as possible to other Replication Servers or replicate databases. By doing this, Replication Server guarantees that every transaction will be successfully received from a Replication Agent is guaranteed to be delivered to appropriately subscribing replicate databases.
Each Replication Server uses a database called the Replication Server System Database (RSSD) to store replication system data and metadata. Sybase Replication Agent can use some of the information stored in the RSSD to provide advanced replication features.