Synchronization replicates application files and configuration information between EJB Servers. It is a useful alternative to importing and exporting packages.
For example, as Figure 4-1 illustrates, you can replicate new packages from a testing or development server to one or more production servers. As long as you can connect to both servers, synchronization is quicker and easier than exporting and importing package files.
Figure 4-1: Synchronization example
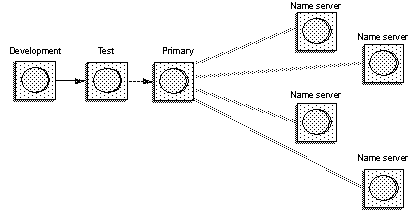
You can use the synchronization option to move repository information between servers. For example, you may want to move a development EJB Server’s repository to a test server. In this case, the synchronization command is similar to export/import options without the JAR file; instead of moving packages from one server to another, you are moving repository information.
You can synchronize at the server or package level. The level you choose determines the available synchronization options. Options that are not available are dimmed, and cannot be selected.