Adaptive Server communicates with other Adaptive Servers, Open Server™ applications (such as Backup Server), and client software on your network. Clients can talk to one or more servers, and servers can communicate with other servers by remote procedure calls.
For Sybase products to interact with one another, each product needs to know where the others reside on the network. Names and addresses of every known server are listed in a directory services file. This information can be stored in a directory services file two different ways:
In an interfaces file, named interfaces on UNIX platforms, located in the $SYBASE installation directory, or
In an LDAP server
After your Adaptive Server or client software is installed, it can connect with any server on the network that is listed in the directory services.
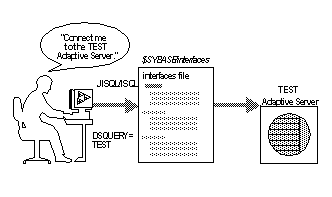
When you are using a client program, and you want to connect with a particular server, the client program looks up the server name in the directory services and connects to that server, as shown in Figure 1-1. You can supply the name of the server by using the DSQUERY environment variable.
On TCP/IP networks, the port number gives clients a way to identify the Adaptive Server, Open Server, Backup Server, or Monitor Server to which they want to connect. It also tells the server where to listen for incoming connection attempts from clients. The server uses a single port for these two services (referred to as query service and listener service).
Figure 1-1: Communicating with a server using the interfaces file
During installation, you use the srvbuild utility to create and configure a new server. The srvbuild process adds entries to the interfaces file for your new Adaptive Server, Backup Server, Monitor Server, and XP Server.
For instructions on how to modify existing interfaces file entries using dsedit and dscp or to create new interfaces file entries for existing servers, Chapter 6, “Using the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol as a Directory Service.”