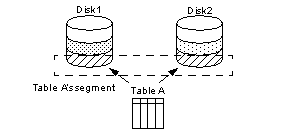
You can split a large, heavily used table across devices on separate disk controllers to improve the overall read performance of a table. When a large table exists on multiple devices, it is more likely that small, simultaneous reads will take place on different disks. Figure 24-2 shows a table that is split across the two devices in its segment.
Figure 24-2: Partitioning a table across physical devices
You can split a table across devices using one of three different methods, each of which requires the use of segments:
Use table partitioning.
If the table has a clustered index, use partial loading.
If the table contains text or image datatypes, separate the text chain from other data.
Partitioning a table creates multiple page chains for the table and distributes those page chains over all the devices in the table’s segment (see Figure 24-2). Partitioning a table increases both insert and read performance, since multiple page chains are available for insertions.
Before you can partition a table, you must create the table on a segment that contains the desired number of devices. The remainder of this chapter describes how to create and modify segments. See Chapter 6, “Controlling Physical Data Placement,” in Performance and Tuning: Basics for information about partitioning tables using alter table.
To split a table with a clustered index, use sp_placeobject with multiple load commands to load different parts of the table onto different segments. This method can be difficult to execute and maintain, but it provides a way to split tables and their clustered indexes across physical devices. See “Placing existing objects on segments” for more information and syntax.
Adaptive Server stores the data for text and image columns on a separate chain of data pages. By default, this text chain is placed on the same segment as the table’s other data. Since reading a text column requires a read operation for the text pointer in the base table and an additional read operation on the text page in the separate text chain, placing the text chain and base table data on a separate physical device can improve performance. See “Placing text pages on a separate device” for more information and syntax.