You can use WHERE and HAVING clauses and retrieval arguments in the SQL SELECT statement for the report to limit the data that is retrieved from the database. This reduces retrieval time and space requirements at runtime.
However, you may want to further limit the data that displays in the report. For example, you might want to:
Retrieve many rows and initially display only a subset
Limit the data that is displayed using InfoMaker expression functions (such as If) that are not valid in the SELECT statement
In the Report painter, you can define filters to limit the rows that display at runtime. Filters can use most InfoMaker expression functions.
![]() Filters do not affect which rows are retrieved
A filter operates against the retrieved data. It does not
re-execute the SELECT statement.
Filters do not affect which rows are retrieved
A filter operates against the retrieved data. It does not
re-execute the SELECT statement.
In the Report painter, select Rows>Filter from the menu bar.
The Specify Filter dialog box displays:
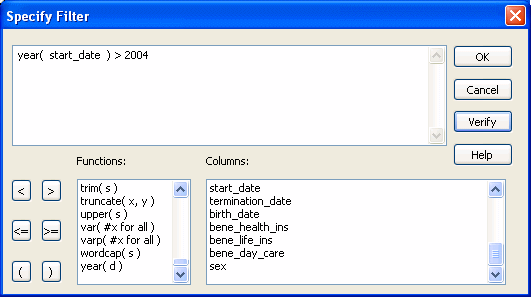
In the Specify Filter dialog box, enter a boolean expression that InfoMaker will test against each retrieved row.
If the expression evaluates to true, the row is displayed. You can specify any valid expression in a filter. You can paste commonly used functions, names of columns, computed fields, retrieval arguments, and operators into the filter.
(Optional) Click Verify to make sure the expression is valid.
Click OK.
Only rows meeting the filter criteria are displayed in the Preview view.
Select Rows>Filter from the menu bar.
Delete the filter expression from the Specify Filter dialog box, then click OK.
Assume that a report retrieves employee rows and three of the columns are Salary, Status, and Emp_Lname. Table 9-1 shows some examples of filters you might use.
To display these rows |
Use this filter |
|---|---|
Employees with salaries over $50,000 |
|
Active employees |
|
Active employees with salaries over $50,000 |
|
Employees whose last names begin with H |
|