If it becomes necessary to switch from the active database to the standby database, you need to take steps to prevent client applications from executing transactions against or updating the active database. After the switch is complete, clients can connect to the new active database to continue their work. See “Switching clients to the new database” for details.
Before switching to a standby database, you should determine whether a switch is necessary:
Don’t switch if the active data server is experiencing a transient failure. A transient failure is a failure from which the Adaptive Server recovers when restarted, without additional recovery steps.
Do switch if the active database will be unavailable for a long period of time.
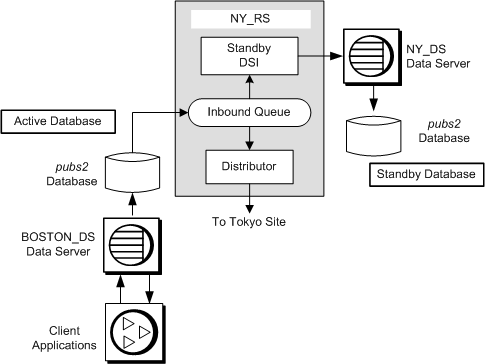
You must use the switch active command to switch the active and standby databases. The following procedure illustrates how to switch the warm standby system illustrated in Figure 3-8 from the active database to the standby database.
On the Replication Server, use switch active to switch processing to the standby database.
Monitor progress of the switch. The switch is complete when the standby connection is active and the previously active connection is suspended.
On the Replication Server, check the logical status, using the admin_logical_status command.
To follow the progress of the switch, check the last several entries in the Replication Server error log.
Start the RepAgent for the new active database.
Decide what you want to do with the old active database. You can:
Bring the database online as the new standby database, and resume connections so that Replication Server can apply new transactions, or
Drop the database connection using the drop connection command. You can add it again later as the new standby database.
Using isql, update a record in the new active database, and then check the update the new standby database.
Figure 3-9: Warm standby system, after switching