The next dialog lets you enable encryption. If you decide to encrypt your database, you must decide on the kind of encryption you want to use, create an encryption key, and decide whether you want to encrypt the entire database or only those tables you specifically mark for encryption.
After you determine the encryption options, click Next.
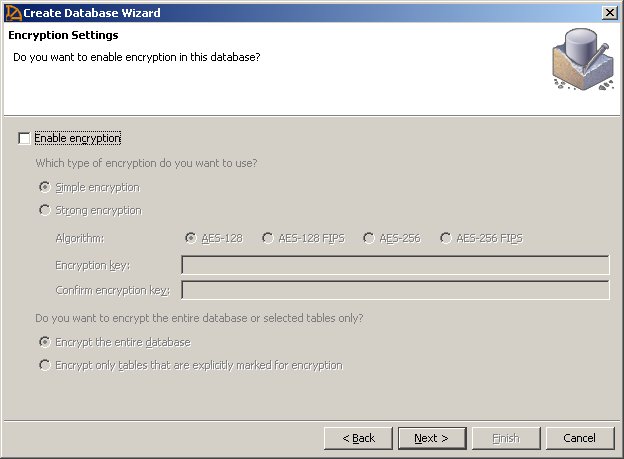
Click the Enable encryption check box to enable encryption.
Simple encryption makes data unreadable, but it could be deciphered by someone with cryptographic expertise. Strong encryption, also called Transport Layer Security (TLS), protects the confidentiality and integrity of network packets as they pass between client and server. Strong encryption uses a 128-bit algorithm and a security key, which is a password you supply.
If you choose Strong encryption, you can either:
Select an algorithm—AES-128, AES-256, or AES-256 FIPS.
Enter an encryption key and then enter it again to confirm. If the two key fields do not match exactly, an error window displays when you press the Next button.
Whichever encryption option you choose, you must select either Encrypt the Entire Database or Encrypt only Tables Explicitly Marked for Encryption.