A physical data model (PDM) helps you to analyze the tables, views, and other objects in a database, including multidimensional objects necessary for data warehousing. A PDM is more concrete than a conceptual (CDM) or logical (LDM) data model. You can model, reverse-engineer, and generate for all the most popular DBMSs.
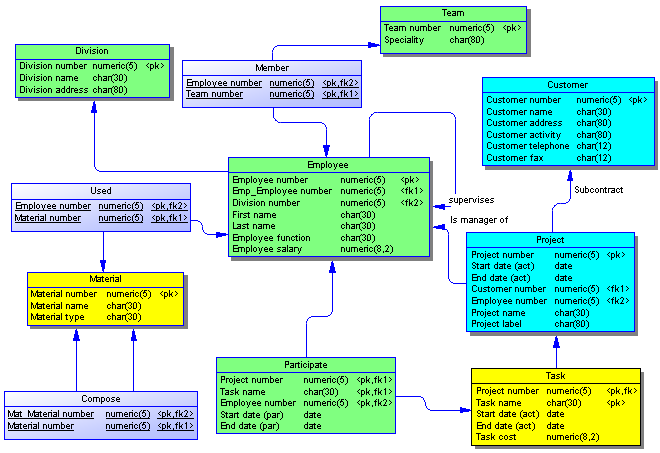
Creating a Physical Data Model
- To create a new, empty PDM, select , and choose Physical Data Model.
- To reverse engineer a new PDM from a live database connection, select .
- To create a new PDM by importing one or more ERwin files, select or .
The following types of diagrams are available:
- A physical data diagram provides a graphical view of your database structure, and helps you analyze its tables (including their columns, indexes, and triggers), views, and procedures, and the references between them.
- A multidimensional data diagram provides a graphical view of your datamart or data warehouse database, and helps you identify its facts, cubes and dimensions.
Specifying a Modeling Notation and Other Options
- To specify a modeling notation, column, reference, and ownership defaults and set other model options, select .
Interacting with Databases
- To connect to a database, select .
- To generate a database, select .
- To modify a database, select .
- To reverse engineer from a live database connection into an existing PDM, select .
- To generate test data to a database, select .
- To estimate the size of a database, select
Generating Other Models
You can generate other PowerDesigner models from a PDM by selecting Tools >:
- Generate Conceptual Data Model (or press Ctrl+Shift+C)
- Generate Logical Data Model (or press Ctrl+Shift+L)
- Generate Physical Data Model (or press Ctrl+Shift+P)
- Generate Object-Oriented Model (or press Ctrl+Shift+O)
- Generate XML Model (or press Ctrl+Shift+M)
Working with DBMS Definitions
The DBMS definition file defines features specific to the DBMS being modeled:
- To open the DBMS definition file in the Resource Editor, select .
- To change the DBMS to model with, select .
Documentation
For detailed documentation, see Data Modeling.