Attributes can be migrated attributes or ordinary attributes. Ordinary attributes can be mapped to columns or formulas. Migrated attributes do not require attribute mapping.
The following types of mapping are possible:
-
Component attribute mapping - A component class can define the attribute mapping as for other classes, except that there is no primary identifier.
-
Discriminator mapping - In inheritance mapping with a one-table-per-hierarchy strategy, the discriminator needs to be specified in the root class. You can define the discriminator in the ADO.NET or ADO.NET CF tab of the class property sheet.
Framework-specific attribute mapping options are defined in the ADO.NET or ADO.NET CF tab of the Attribute property sheet.
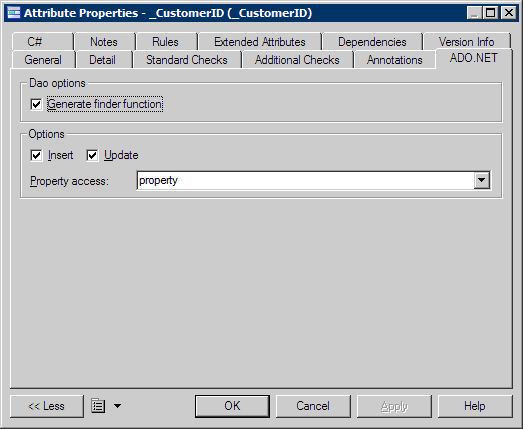
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Generate finder function |
Generates a finder function for the attribute. |
|
Insert |
Specifies that the mapped columns should be included in any SQL INSERT statements. |
|
Update |
Specifies that the mapped columns should be included in any SQL UPDATE statements. |
|
Lazy |
Specifies that this property should be fetched lazily when the instance variable is first accessed (requires build-time byte code instrumentation). |
|
Property access |
Specifies the strategy used for accessing the property value. |