The data cache holds the data, index, and log pages that are currently in use, as well as pages used recently by SAP ASE.
Immediately after installation, SAP ASE has a single default data cache that is used for all data, index, and log activity. The default size of this cache is 8M. Creating other caches does not reduce the size of the default data cache. Also, you can create pools within the named caches and the default cache to perform large I/Os. You can then bind a database, table (including the syslogs table), index, or text or image page chain to a named data cache.
Large I/O sizes enable SAP ASE to perform data prefetching when the query optimizer determines that prefetching would improve performance. For example, an I/O size of 128K on a server configured with 16K logical pages means that SAP ASE can read an entire extent—8 pages—all at once, rather than performing 8 separate I/Os.
Sorts can also take advantage of buffer pools configured for large I/O sizes.
Configuring named data caches does not divide the default cache into separate cache structures. The named data caches that you create can be used only by databases or database objects that are explicitly bound to them. All objects not explicitly bound to named data caches use the default data cache.
SAP ASE provides user-configurable data caches to improve performance, especially for multiprocessor servers.
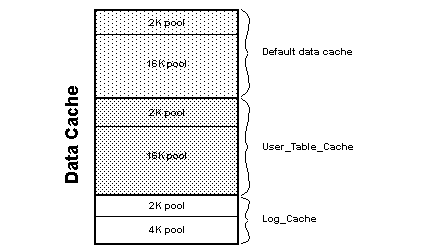
This figure shows a cache with the default data cache and two named data caches. This server uses 2K logical pages.
The default cache contains a 2K pool and a 16K pool. The User_Table_Cache cache also has a 2K pool and a 16K pool. The Log_Cache has a 2K pool and a 4K pool.