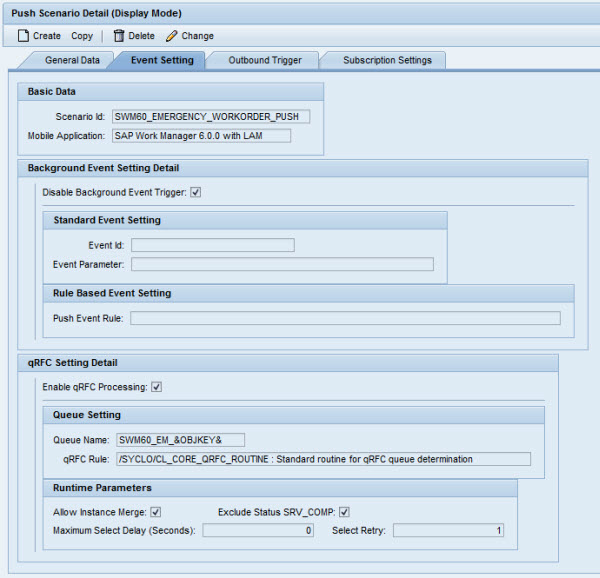
Push Scenario Definition - Event Setting
Use the Event Setting tab of the Push Scenario Detail screen to control how the push processing is triggered for specific events when data is changed in SAP and triggers a push. Event settings can be set using variables or by assigning specific events or queues to initiate the push process.
You can initiate push processing either via an SAP background event or via an SAP qRFC. Each of these options is described in the appropriate section following the “Push Scenario Definition - Event Setting Tab” screen shot.
Basic Data
- Scenario ID: Name of the push scenario
- Mobile Application: Application to which the push scenario belongs
Background Event Setting Detail
Complete this section to enable push processing via an SAP background event.
If you enable this option, an SAP background event is raised after a push instance is registered with the push registry. The event can subsequently start an SAP background job that is subscribed to the background event. The started SAP background job can process new push instances in the push registry.
- Disable Background Event Trigger: Uncheck this box when using the Background Event Setting Detail fields. When checked, the push process is triggered by the information configured here, rather than by the background event and no background event is raised after the push instance is registered with the push registry.
- Event ID: Either a static or variable event ID to be raised. For information on variables, hover over the field to read the tool tip that appears. Event IDs are used to determine when to raise the event.
- Event Parameter: A free-text field to configure parameters associated with the Event ID when raised. Parameters can be static or use variables. For information on variables, hover over the field to read the tool tip that appears. Typical parameters can be push scenario IDs, etc.
- Push Event Rule: This is a special ABAP class routine that returns the Event ID and event parameters programmatically. A standard routine is provided, but a custom routine can be developed by the customer if there is a business need.
Special variables can be used when defining the Event ID. Special variables are substituted at runtime. If special variables are used, the push event rule must be defined in order for the substitution to occur. Special variables include the following:
- &OBJKEY&
- &OBJKEY_REF&
- &MOBILE_APP&
- &INSTANCE_GUID&
- &SCENARIO_ID&
- &SOURCE_OBJECT&
- &SOURCE_TYPE&
- &DATUM&
- &UZEIT&
- &UNAME&
- &HOST&
Monitoring SAP background event trigger by push instances
To monitor the SAP push, use the following tools:
- Go to the Administration & Monitoring Portal -> Monitoring -> Push Instance Monitor and search for push instances using proper search filters. Verify the Event ID and the event parameter of the push instance.
- Use the transaction code SM37 to search and verify that SAP background jobs are being triggered properly by the Event ID and the event parameters raised during the push process.
qRFC Setting Detail
Complete this section to enable push processing via SAP qRFC.
If you enable this option, after a push instance is registered with the push registry, a new entry is added to the SAP qRFC queue for the specific push instance. The qRFC queue entry is processed automatically by the SAP system. When the qRFC queue is processed, the specific push instance is processed by the push processor.
- Enable qRFC Processing: When checked, enables initiating the push process through the qRFC queue.
- Queue Name: Either a static or a variable qRFC queue name.
- qRFC Rule: This is a special ABAP class routine that returns the qRFC queue name programmatically. A standard routine is provided, but a custom routine can be developed by the customer if there is a business need.
- Allow Instance Merge: When checked, if multiple processes are triggered on the same SAP object, the instances are merged to save processing time.
- Exclude Status SRV_COMP: When checked, push instances with SRV_COMP status are not reprocessed.
- Maximum Select Delay: This is the number of seconds to wait before reading from the push registry DB table. This is only needed for slow systems. This is typically set to 1 or 0. If the system takes longer to write to the database, set to higher than 1.
- Select Retry: Number of times to retry the select from DB table is nothing is found. This is only needed for slow systems.
- &OBJKEY&
- &OBJKEY_REF&
- &MOBILE_APP&
- &INSTANCE_GUID&
- &SCENARIO_ID&
- &SOURCE_OBJECT&
- &SOURCE_TYPE&
- &DATUM&
- &UZEIT&
- &UNAME&
- &HOST&
Monitoring push instance processing via SAP qRFC
To monitor the SAP push, use the following tools:
- Go to the Administration & Monitoring Portal -> Monitoring -> Push Instance Monitor and search for push instances using proper search filters. Verify the qRFC queue name of the push instance.
- Use the transaction code SMQ1 to search and verify that there are not outstanding entries waiting in the qRFC queue.
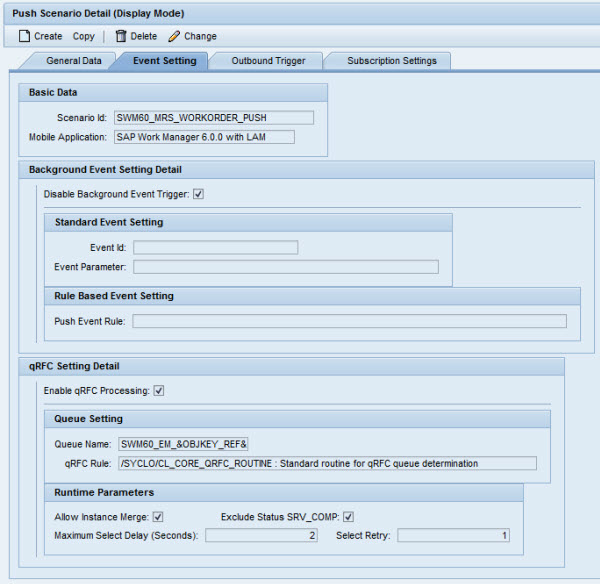
Example
The following sample screen shows that a push is enabled via the SAP qRFC queue.