Sybase Mobile SDK supports the development lifecycle for Object API Applications, HTML5/JS Hybrid Apps, and OData SDK Applications.
The end result of the development process is a packaged mobile application
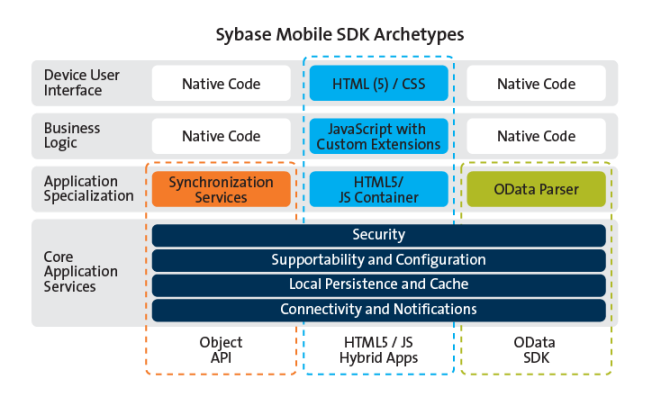
ready for provisioning to devices. The following diagram shows the device application
structure and services provided for each of the development approaches with Sybase
Mobile SDK.
Dashed outlines in
the diagram represent the services provided by Sybase Mobile SDK for each application
archetype. Native code development takes place in a third party development tool, such
as Visual Studio, Eclipse, etc., outside of the Mobile SDK. Native code development uses
Unwired Platform APIs that support core services and application specialization, in
addition to leveraging in-house device platform development expertise.
- Core Application Services – The set of common services provides a consistent foundation upon which mobile
apps are developed. These common device services make development easier and
more efficient in developing multiple applications.
Security features are embedded into the SDK to support secure storage of certificates, use of the artifacts in authentication, single sign-on, and other features related to encryption of the database. APIs are supplied to support certificate store, logon certificate, and the data vault. Each application type makes use of the same set of security features.
Supportabilty and configuration allow developers to enable and configure exception reporting within the mobile application so that device users and developers can identify and troubleshoot issues.
Local persistence and cache management define how the application stores and receives/retrieves data and interacts with the middleware.
Connectivity and notifications facilitate online/offline connections and push notifications to device users.
- Application Specialization – Application specialization is the differentiator between development approaches. Based on these distinct application services and your business needs, develop one or more application types.
Develop Apps with When your business needs Native Object API SDK Offline applications: Mission-critical and more complex. Users work on data offline and synchronize updates to the server when connected. HTML5/JS Hybrid App SDK Online applications with Push: Simple queries and workflows that follow a request-reply or lookup pattern. OData SDK Online applications with Push that use OData protocol: Data, modeled in SAP NetWeaver Gateway, is accessed in a request-reply or lookup pattern. Synchronization implies an intermediary store of cached data and the process by which data changes are propagated between the server, the cache, and the device storage with the goal of ensuring that the data is replicated in each location.
Push leverages a proprietary message transport to move data between device and server. The data change is initiated, or pushed, from where ever the data change takes place: from the device if the change takes place there, or from the server if the change takes place there.
- Business Logic and Device User Interface – The user interface is developed:
- Using the developer IDE of choice for the target device platform and either the Object API or the OData SDK API.
- Using the Mobile Workflow Forms Editor to design HTML5/JS.
The following sections provide detail about the development lifecycle and about each type of archetype development.