Sybase IQ multiplexes have a hybrid cluster architecture that involves shared storage for permanent IQ data and independent node storage for catalog metadata, temporary data, and transaction logs.
Sybase IQ multiplex:
Lets you manage large workloads across multiple nodes.
Allows data loads from multiple writer nodes.
Lets shared database objects be written by one user and queried by multiple users simultaneously. Many objects of this type may exist and be in use at the same time in the database.
Offers high availability. Failures of a single node leave others up and running.
Reduces the cost of data by sharing it. Adding systems to the array provides more CPU power and memory space for processing queries if the workload is balanced effectively across the multiplex nodes.
Sybase IQ's column stores reduce I/O requirements, enabling many systems to share the disk array(s) without degrading performance due to I/O contention.
Sybase IQ supports read-write transactions from multiple servers in the multiplex. The primary server, or coordinator, manages all global read-write transactions and maintains the global catalog. The table version log (TLV log) stores information about DDL operations and communicates information about new table versions to the secondary servers.
The configuration can be described as an “asymmetrical cluster,” because node capabilities may differ, unlike other database cluster architectures, which usually follow either a “shared everything” or “shared nothing” architecture.
Figure 1-2: IQ multiplex architecture
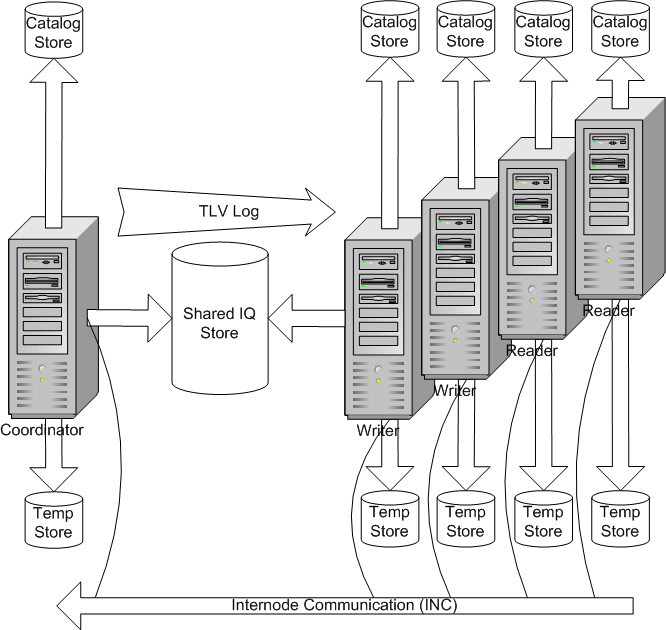
Each server has its own temporary store and catalog store.
The shared IQ store is common to all servers.