 Create the consolidated database and directories for the tutorial
Create the consolidated database and directories for the tutorialCreate the directories c:\tutorial, c:\tutorial\hq, and c:\tutorial\field.
From the c:\tutorial directory, run the following command to create the consolidated database (hq):
dbinit hq.db |
Connect to the consolidated database (hq) from Interactive SQL.
dbisql -c "UID=DBA;PWD=sql;SERVER=server_hq;DBF=c:\tutorial\hq.db" |
Execute the following statements to create two tables in the consolidated database (hq):
CREATE TABLE SalesReps ( rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL, name CHAR(40) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY ( rep_key ) ); CREATE TABLE Customers ( cust_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL, name CHAR(40) NOT NULL, rep_key CHAR(12) NOT NULL, FOREIGN KEY ( rep_key ) REFERENCES SalesReps (rep_key ), PRIMARY KEY (cust_key) ); |
The following figure shows the consolidated database (hq) schema for the tutorial:
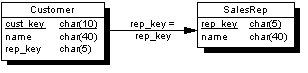
Each sales representative is represented by one row in the SalesReps table.
Each customer is represented by one row in the Customers table.
Each customer is assigned to a single sales representative, and this assignment is built into the database as a foreign key from the Customers table to the SalesReps table. The relationship between the Customers table and the SalesReps table is many-to-one.
| Table name | Description |
|---|---|
| SalesRep |
In the SalesReps table, there is a row for each sales representative that works for the company. The SalesReps table has the following columns:
|
| Customers |
In the Customers table, there is one row for each customer that does business with the company. The Customers table includes the following columns:
|
Execute the following statements to add sample data to the SalesReps and Customers tables:
INSERT INTO SalesReps (rep_key, name)
VALUES ('rep1', 'Field User');
INSERT INTO SalesReps (rep_key, name)
VALUES ('rep2', 'Another User');
COMMIT;
INSERT INTO Customers (cust_key, name, rep_key)
VALUES ('cust1', 'Ocean Sports', 'rep1' );
INSERT INTO Customers (cust_key, name, rep_key)
VALUES ('cust2', 'Sports Plus', 'rep2' );
COMMIT; |
Execute the following statements to confirm that the tables were created:
SELECT * FROM SalesReps; |
The above query returns the following data from the SalesReps table:
| rep_key | name |
|---|---|
| rep1 | Field User |
| rep2 | Another User |
SELECT * FROM Customers; |
The above query returns the following data from the Customers table:
| cust_key | name | rep_key |
|---|---|---|
| cust1 | Ocean Sports | rep1 |
| cust2 | Sports Plus | rep2 |
 |
Discuss this page in DocCommentXchange.
|
Copyright © 2012, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 12.0.1 |