Allows you to resolve referential integrity violations in the download process.
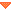 Rows in #hook_dict table
Rows in #hook_dict table| Name | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
publication_n (in) |
publication |
Deprecated. Use subscription_n instead. The publications being synchronized, where n is an integer. There is one publication_n entry for each publication being synchronized. The numbering of n starts at zero. |
|
MobiLink user (in) |
MobiLink user name |
The MobiLink user for which you are synchronizing. |
|
foreign key table (in) |
table name |
The table containing the foreign key column for which the hook is being called. |
|
primary key table (in) |
table name |
The table referenced by the foreign key for which the hook is being called. |
|
role name (in) |
role name |
The role name of the foreign key for which the hook is being called. |
|
script version (in) |
script version name |
The MobiLink script version to be used for the synchronization. |
| subscription_n (in) | subscription name(s) | The names of subscriptions being synchronized where n is an integer. This is one subscription_n entry for each subscription being synchronized. The numbering of n starts at zero. |
 Remarks
RemarksA download RI violation occurs when rows in the download violate foreign key relationships on the remote database. This hook allows you to attempt to resolve RI violations before dbmlsync deletes the rows that are causing the conflict.
After the download is complete, but before it is committed, dbmlsync checks for RI violations. If it finds any, it identifies a foreign key that has an RI violation and calls sp_hook_dbmlsync_download_log_ri_violation (if it is implemented). It then calls sp_hook_dbmlsync_download_ri_violation (if it is implemented). If there is still a conflict, dbmlsync deletes the rows. This process is repeated for remaining foreign keys that have RI violations.
This hook is called only when there are RI violations involving tables that are currently being synchronized. If there are RI violations involving tables that are not being synchronized, this hook is not called and the synchronization fails.
This hook is called on the same connection that dbmlsync uses for the download. This hook should not contain any explicit or implicit commits, because they may lead to inconsistent data in the database. The actions of this hook are committed or rolled back when the download is committed or rolled back.
Unlike other hook actions, the operations performed during this hook are not uploaded during the next synchronization.
 See also
See also Example
ExampleThis example uses the Department and Employee tables shown below:
CREATE TABLE Department( "department_id" INTEGER primary key ); CREATE TABLE Employee( "employee_id" INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, "department_id" INTEGER, FOREIGN KEY EMPLOYEE_FK1 (department_id) REFERENCES Department ); |
The following sp_hook_dbmlsync_download_ri_violation definition cleans up referential integrity violations between the Department and Employee tables. It verifies the role name for the foreign key and inserts missing department_id values into the Department table.
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_hook_dbmlsync_download_ri_violation() BEGIN IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM #hook_dict WHERE name = 'role name' AND value = 'EMPLOYEE_FK1') THEN -- update the Department table with missing department_id values INSERT INTO Department SELECT distinct department_id FROM Employee WHERE department_id NOT IN (SELECT department_id FROM Department) END IF; END; |
 |
Discuss this page in DocCommentXchange.
|
Copyright © 2012, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 12.0.1 |