This example shows how the auditing feature records attempts to access unauthorized information using either Sybase Central or Interactive SQL.
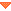 Sybase Central auditing example
Sybase Central auditing exampleStart Sybase Central and connect to the sample database using the SQL Anywhere 12 Demo data source.
This connects you as a user with DBA authority.
Turn on auditing:
Right-click the database and click Properties.
Click the Auditing tab.
Click Collect All Audit Information For This Database.
Click Apply.
Click OK.
Add a user named Test1 to the sample database, with the password welcome:
Right-click Users & Groups, and click New » User.
When prompted, name the user Test1, and type welcome as their password.
Give the user Profile Authority.
Click Finish.
Disconnect from the sample database.
Using Sybase Central, connect to the sample database as Test1 and attempt to access confidential information in the Employees table:
Click Tables, and then select the Employees table.
Click the Data tab.
An error message appears indicating that you do not have permission to select from the Employees table. See Permission denied: %1.
Click OK.
Disconnect from the sample database.
View the auditing information for this activity:
Using Sybase Central, connect to the sample database as a user with DBA authority.
Select the database, and then click the Auditing tab in the right pane.
Click Retrieve Audit Messages.
Click Close.
Auditing information appears.
Use the filtering options to locate the error in the auditing information table. You can find the error for Test1 by selecting the Only Errors option. Use the date and time information to pinpoint the error. For example, if Test1 tried accessing the Employees table on November 6, 2007 at 10:07:14, the corresponding audit entry resembles the following entry:
2007-11-06 10:07:14 | Permission |
Restore the sample database to its original state:
Right-click the database, and then click Properties.
On the Auditing tab, click Do Not Collect Audit Information For This Database.
Click OK.
Click Users & Groups.
Right-click Test1, and click Delete.
 Interactive SQL auditing example
Interactive SQL auditing exampleStart Interactive SQL and connect to the sample database using the SQL Anywhere 12 Demo data source.
This connects you as a DBA user.
Turn on auditing using the SET OPTION statement, as follows:
SET OPTION PUBLIC.auditing = 'On'; |
Add a user, Test1, to the sample database using the CREATE USER statement, as follows:
CREATE USER Test1 IDENTIFIED BY welcome; |
Open a new Interactive SQL window, connect to the sample database as Test1, and attempt to access confidential information in the Employees table using the following SELECT statement:
SELECT Surname, Salary FROM GROUPO.Employees; |
An error message appears indicating that you do not have permission to select from the Employees table. See Permission denied: %1.
Run the following command to view the auditing information for this activity:
dbtran -g -c "DSN=SQL Anywhere 12 Demo" -n demo.sql |
Restore the sample database to its original state:
Use the DROP USER statement to remove the Test1 user from the database:
DROP USER Test1; |
Turn off auditing using the following SET OPTION statement:
SET OPTION PUBLIC.auditing = 'Off'; |
 |
Discuss this page in DocCommentXchange.
|
Copyright © 2012, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 12.0.1 |