Sets the format for dates retrieved from the database.
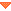 Allowed values
Allowed valuesString
 Default
DefaultYYYY-MM-DD
 Scope
ScopeCan be set for an individual connection or for the PUBLIC group. Takes effect immediately.
 Remarks
RemarksThe format is a string using the following symbols:
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| YY | Two-digit year |
| YYYY | Four-digit year |
| MM | Two-digit month |
| MMM[m...] | Character short form for months |
| D | Single digit day of week (1 = Sunday, 7 = Saturday) |
| DD | Two-digit day of month |
| DDD[d...] | Character short form for days of the week |
| JJJ | Day of the year, from 1 to 366 |
Each symbol is substituted with the appropriate data for the date that is being formatted.
For more information about controlling the interpretation of date formats, see date_order option.
If the character data is multibyte, the length of each symbol reflects the number of characters, not the number of bytes. For example, the 'mmm' symbol specifies a length of three characters for the month.
For symbols that represent character data (such as mmm), you can control the case of the output as follows:
Type the symbol in all uppercase to have the format appear in all uppercase. For example, MMM produces JAN.
Type the symbol in all lowercase to have the format appear in all lowercase. For example, mmm produces jan.
Type the symbol in mixed case to have SQL Anywhere choose the appropriate case for the language that is being used. For example, in English, typing Mmm produces May, while in French it produces mai.
For symbols that represent numeric data, you can control zero-padding with the case of the symbols:
Type the symbol in same-case (such as MM or mm) to allow zero padding. For example, yyyy/mm/dd could produce 2002/01/01.
Type the symbol in mixed case (such as Mm) to suppress zero padding. For example, yyyy/Mm/Dd could produce 2002/1/1.
If you change the setting for date_format in a way that re-orders the date format, be sure to change the date_order option to reflect the same change, and vice versa. See date_order option.
 See also
See also Example
ExampleThe following table illustrates date_format settings, together with the output from the following statement, executed on Monday, April 14, 2008.
SELECT CAST( CURRENT DATE AS VARCHAR ); |
| date_format | CURRENT DATE |
|---|---|
| yyyy/mm/dd/ddd | 2008/04/14/mon |
| yyyy/Mm/Dd/ddd | 2008/4/14/mon |
| jjj | 105 |
| mmm yyyy | apr 2008 |
| Mmm yyyy | Apr 2008 |
| mm-yyyy | 04-2008 |
 |
Discuss this page in DocCommentXchange.
|
Copyright © 2012, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 12.0.1 |