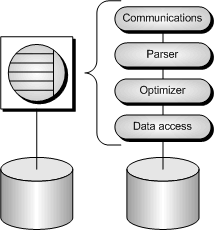
The SQL Anywhere database server has an internal structure that allows many requests to be handled efficiently.
A communications layer handles the exchange of data with client applications. This layer receives requests from client applications, and returns results. The timing of these actions is governed by a negotiation between the client and the server to make sure that the network traffic is kept to a minimum, but that the data is made available as soon as possible on the client side.
The parser checks each SQL statement sent to the database server, and transforms it into an internal form for processing.
If the request is a query, an update, or delete statement, there can be many different ways of accessing the data, which may take significantly different times. The optimizer selects the best method of getting the required data quickly.
The lowest level of the database server is concerned with reading and writing data from the disk, caching data in memory to avoid unnecessary disk access, and balancing the demands of different users.
 Two types of SQL Anywhere database servers
Two types of SQL Anywhere database servers |
Discuss this page in DocCommentXchange.
|
Copyright © 2010, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 12.0.0 |