A relational database management system (RDBMS) is a system for storing and retrieving data, in which the data is organized into interrelated tables.
Relational database management systems contain the following pieces:
Database Data is stored in a database. In diagrams in the documentation, a database is indicated by a cylinder:
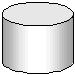
A SQL Anywhere database is a file, usually with an extension of .db. An UltraLite database is also a file, usually with an extension of .udb. SQL Anywhere includes a sample database for you to work with, and it is installed in the SQL Anywhere samples directory: samples-dir\demo.db.
For information about the default location of samples-dir, see Samples directory.
Database server The database server manages the database. All access to the database occurs through the database server.
The database server allows access to databases from client applications, and processes commands in a secure and efficient manner. A database can have only one server managing it at a time. However, a SQL Anywhere database server can manage many databases at one time.
In the documentation, a database server is indicated as follows:
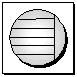
There are two versions of the SQL Anywhere database server: the personal server and the network server. Both servers offer the same query processing and other internal operations; the only difference is in the number and types of connections each server accepts.
The personal server only accepts a maximum of ten concurrent connections from applications or users running on the same computer. It is intended for single-user, same-computer use.
By contrast, the network server supports client/server communication over a network and is intended for multi-user, multi-computer use. The maximum number of connections is governed by your license agreement.
See Two types of SQL Anywhere database servers.
UltraLite runtime library In UltraLite, the database management systems that are typically found in a database server are implemented as an in-process runtime library. The runtime library and the application are part of the same process.
Programming interface Applications communicate with the database server using a programming interface such as ODBC, JDBC, OLE DB, ADO.NET, or embedded SQL.
For a complete list of supported programming interfaces in SQL Anywhere and UltraLite, see Programming interfaces.
Each programming interface provides a library of function calls for communicating with the database. For ODBC and JDBC, the library is commonly called a driver. The library is typically provided as a shared library on Unix operating systems or a dynamic link library (DLL) on Windows operating systems.
In diagrams in the documentation, a programming interface is indicated as follows:

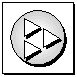
Client application Client applications use one of the programming interfaces to communicate with the database server.
If you develop an application using a rapid application development (RAD) tool such as Sybase PowerBuilder, you may find that the tool provides its own methods for communicating with database servers, and hides the details of the language interface. Nevertheless, all applications use one of the supported interfaces.
In diagrams in the documentation, a client application is indicated as follows:
| Discuss this page in DocCommentXchange. Send feedback about this page using email. |
Copyright © 2009, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 11.0.1 |