Use this tutorial to learn how to use the Application Profiling Wizard to create a baseline that you can use for comparison purposes when improving performance.
Procedure profiling provides execution time measurements for procedures, user-defined functions, events, system triggers, and triggers. You can set your saved results as a baseline and make incremental changes to the procedure and run it after each change you make. This allows you to compare the new results to the baseline.
This tutorial assumes you have followed the setup steps for the application profiling tutorials. If you have not, see Setting up for the application profiling tutorials.
You can copy and paste the SQL statements in this tutorial into Interactive SQL.
To create a baseline procedure
Start Sybase Central and connect to the test database app_profiling - DBA with the user ID DBA and the password sql.
If you have not created the test database, see Setting up for the application profiling tutorials.
If you are unfamiliar with starting Sybase Central and connecting to a database, see Connecting to a database on your own computer from Sybase Central or Interactive SQL.
In the left pane, select the app_profiling - DBA database, and then choose File » Open Interactive SQL.
Interactive SQL starts and connects to the app_profiling - DBA database.
In Interactive SQL, run the following SQL statements:
CREATE TABLE table1 ( Count INT ); |
CREATE PROCEDURE baseline( )
BEGIN
INSERT table1
SELECT COUNT (*)
FROM rowgenerator r1, rowgenerator r2,
rowgenerator r3
WHERE r3.row_num < 5;
END; |
COMMIT; |
Close Interactive SQL.
To run an updated procedure against the baseline procedure
In Sybase Central, choose Mode » Application Profiling.
If the Application Profiling Wizard does not appear, choose Application Profiling » Open Application Profiling Wizard.
On the Welcome page, click Next.
On the Profiling Options page, select Stored Procedure, Function, Trigger, Or Event Execution Time.
Click Finish.
The database server begins procedure profiling.
In the left pane of Sybase Central, double-click Procedures & Functions.
Right-click the baseline procedure and choose Execute From Interactive SQL. Procedure profiling is enabled, so execution details for the procedure are captured.
Close Interactive SQL.
View the profiling results.
The execution times appear for each line in the baseline procedure.
Save the profiling results.
The App_Profiling - DBA Database Properties window appears.
The procedure profiling information that was just gathered is saved to the specified profiling log file (.plg).
Enable baselining against the profiling log file.
Make changes to the baseline procedure.
INSERT table1 SELECT COUNT ( * ) FROM rowgenerator r1, rowgenerator r2, rowgenerator r3 WHERE r3.row_num < 250; |
In Procedures & Functions, right-click the baseline procedure and choose Execute From Interactive SQL.
Exit Interactive SQL when the procedure completes.
To compare the procedure profiling results
In Sybase Central, choose Mode » Application Profiling.
If the Application Profiling Wizard appears, click Cancel.
In the left pane of Sybase Central, in Procedures & Functions, click the baseline procedure.
In the right pane, click the Profiling Results tab.
Choose View » Refresh Folder.
Two new columns, Execs. +/- and ms. +/-, appear.
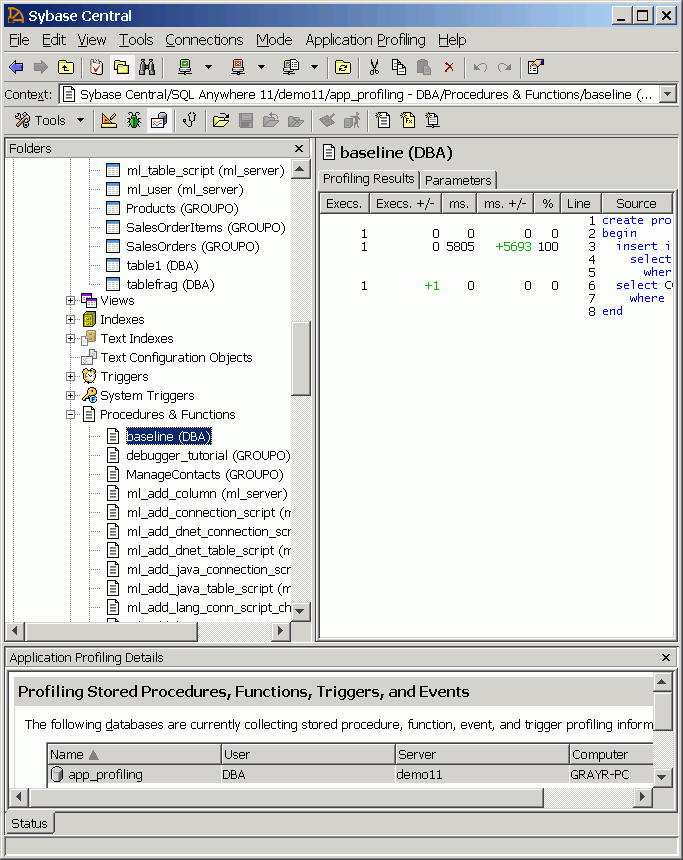
The Execs. +/- and ms. +/- columns result from comparing statistics in the profiling log file to the statistics captured during the most recent execution of the procedure. Specifically, they compare number of executions and duration of execution, respectively, for each line of code in the procedure.
Typically, you are interested in the ms. +/- column, which indicates whether you improved the execution time for lines of code in the procedure. Faster times are indicated by a minus sign and red font. Slower times are indicated by no sign, and green font. In this tutorial, the value in the ms. +/- column should be a + sign along with a execution time in green font. The INSERT statement in the updated procedure has a slower time than the INSERT statement in the baseline procedure.
| Send feedback about this page via email or DocCommentXchange | Copyright © 2008, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 11.0.0 |