SQL Anywhere supports a large subset of Transact-SQL, the dialect of SQL supported by Sybase Adaptive Server Enterprise. This chapter describes compatibility of SQL between SQL Anywhere and Adaptive Server Enterprise.
The goals of Transact-SQL support in SQL Anywhere are as follows:
Application portability Many applications, stored procedures, and batch files can be written for use with both Adaptive Server Enterprise and SQL Anywhere databases.
Data portability SQL Anywhere and Adaptive Server Enterprise databases can exchange and replicate data between each other with minimum effort.
The aim is to write applications to work with both Adaptive Server Enterprise and SQL Anywhere. Existing Adaptive Server Enterprise applications generally require some changes to run on a SQL Anywhere database.
Transact-SQL support in SQL Anywhere takes the following form:
The following diagram illustrates how the two dialects overlap.
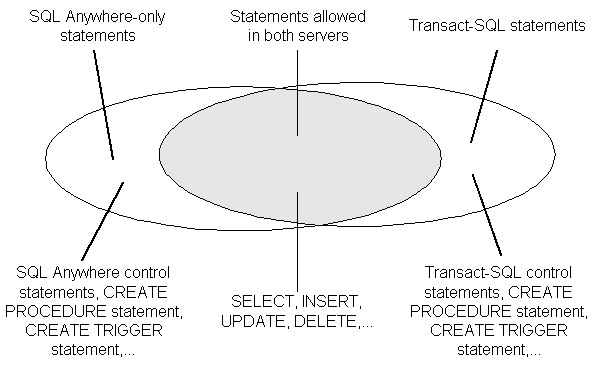
SQL Anywhere supports a very high percentage of Transact-SQL language elements, functions, and statements for working with existing data. For example, SQL Anywhere supports all of the numeric functions, all but one of the string functions, all aggregate functions, and all date and time functions. As another example, SQL Anywhere supports extended DELETE and UPDATE statements using joins.
Further, SQL Anywhere supports a very high percentage of the Transact-SQL stored procedure language (CREATE PROCEDURE and CREATE TRIGGER syntax, control statements, and so on) and many, but not all, aspects of Transact-SQL data definition language statements.
There are design differences in the architectural and configuration facilities supported by each product. Device management, user management, and maintenance tasks such as backups tend to be system-specific. Even here, SQL Anywhere provides Transact-SQL system tables as views, where the tables that are not meaningful in SQL Anywhere have no rows. Also, SQL Anywhere provides a set of system procedures for some of the more common administrative tasks.
This chapter looks first at some system-level issues where differences are most noticeable, before discussing data manipulation and data definition language aspects of the dialects where compatibility is high.
Some SQL statements supported by SQL Anywhere are part of one dialect, but not the other. You cannot mix the two dialects within a procedure, trigger, or batch. For example, SQL Anywhere supports the following statements, but as part of the Transact-SQL dialect only:
Adaptive Server Enterprise does not support the following statements:
The two dialects cannot be mixed within a procedure, trigger, or batch. This means that:
| Send feedback about this page via email or DocCommentXchange | Copyright © 2008, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 11.0.0 |