ACME Corporation is a small company with offices in five locations. Currently, 75 employees work for ACME. The company is preparing for rapid growth and has identified nine departments, each with its own department head.
To help in its search for new employees, the personnel department has identified 68 skills that it believes the company will need in its future employee base. When an employee is hired, the employee's level of expertise for each skill is identified.
Some of the high-level activities for ACME Corporation are:
Identify the entities (subjects) and the relationships (roles) that connect them. Create a diagram based on the description and high-level activities.
Use boxes to show entities and lines to show relationships. Use the two roles to label each relationship. You should also identify those relationships that are one-to-many, one-to-one, and many-to-many using the appropriate annotation.
Following is a rough entity-relationship diagram. It will be refined throughout the example.
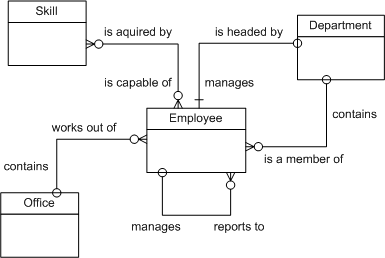
The following lower-level activities below are based on the high-level activities listed above:
These lower-level activities can be used to identify if any new tables or relationships are needed.
Business rules often identify one-to-many, one-to-one, and many-to-many relationships.
The kind of business rules that may be relevant include the following:
| Send feedback about this page via email or DocCommentXchange | Copyright © 2008, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 11.0.0 |