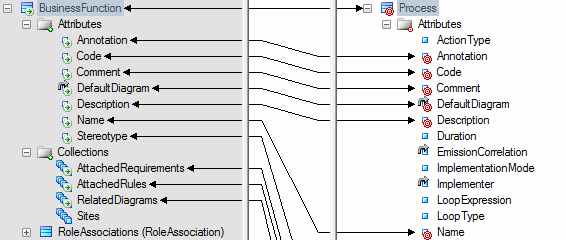
You control how metaclasses from one PowerDesigner model type will be generated to metaclasses in another model type by mapping them and their attributes and collections in the Mapping Editor. Any extensions defined for the source or target metamodels are displayed and available for mapping.
Note: It is not necessary to map all metaclasses (or all their contents), but only those
with which you want to work. If the PowerDesigner metamodel does not contain
appropriate metaclasses, attributes, compositions, or aggregations to map against,
you should save any existing mappings, close the Mapping Editor, define or attach
appropriate extensions, and then reopen the Mapping Editor to map to them.