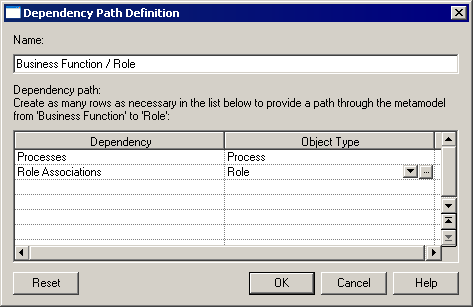
You can examine dependencies between two types of objects that are not directly associated with each other, using the Dependency Path Definition dialog, which is accessible by clicking the Advanced button on the Definition tab, and which allows you to specify a path passing through as many intermediate linking objects as necessary.
Each line in this dialog represents one step in a dependency path:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Specifies a name for the dependency path. By default, this field is populated with the origin and destination object types. |
| Dependency | Specifies the dependency for this step in the path. The list is populated with all the possible dependencies for the previous object type. |
| Object Type | Specifies the specific object type that is linked to the previous object type by the selected dependency. This field is autopopulated if only one object type is available through the selected dependency. |
In the following example, a path is identified between business functions and roles, by passing from the business function through the processes it contains, to the role linked to it by a role association: