The type of key that is generated in the PDM depends on the cardinality and type of dependency defined for a relationship in the CDM. Primary identifiers generate primary and foreign keys. Other identifiers that are not primary identifiers generate alternate keys:
-
A primary key is a column or columns whose values uniquely identify a row in a table.
-
A foreign key is a column or columns that depend on and migrate from a primary key column in another table.
-
An alternate key is a column or columns whose values uniquely identify a row in a table, and is not a primary key.
Independent One-to-many Relationships
In independent one-to-many relationships, the primary identifier of the entity on the one side of the relationship is generated as a:
The following CDM shows an independent relationship. Each division contains one or more employees:
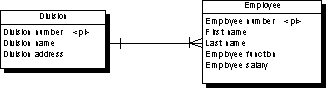
The following PDM will be generated:
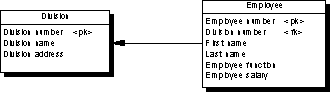
Dependent One-to-many Relationships
In dependent relationships, the primary identifier of the nondependent entity is generated as a primary/foreign key in the table generated by the dependent entity. The migrated column is integrated into the primary key if it already exists.
The following CDM shows a dependent relationship. Each task must have a project number.
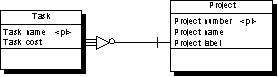
The following PDM will be generated:
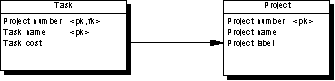
Independent Many-to-many Relationships
In independent many-to-many relationships, the primary identifiers of both entities migrate to a join table as primary/foreign keys. The CDM below shows an independent relationship. Each employee can be a member of one or more teams, and each team can have one or more employees as members.
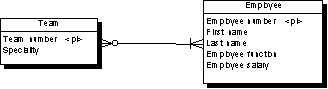
The following PDM will be generated:
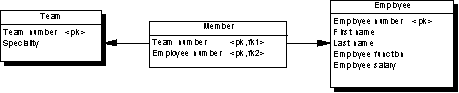
|
Table |
Primary key |
Foreign key |
|---|---|---|
|
Team |
Team number |
— |
|
Employee |
Employee number |
— |
|
Member |
Team number/Employee number |
Team number/Employee number |