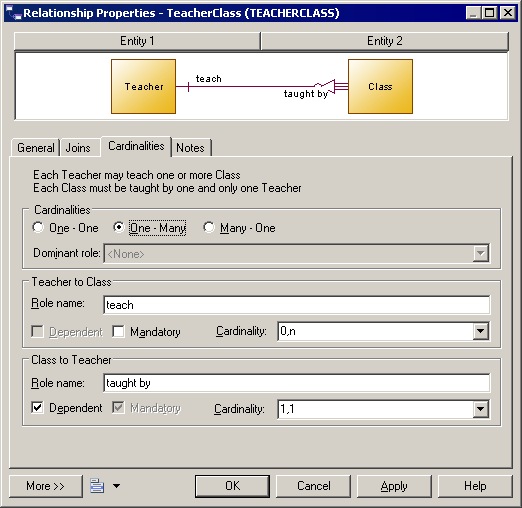
The Cardinalities tab allows you to specify the nature of the relationship between the two entities.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Cardinality |
Specifies the number of instances (none, one, or many) of an entity in relation to another entity. You can choose from the following values:
|
|
Dominant role |
[one-to-one relationships only] Specifies one direction of the relationship as dominant. If you define a dominant direction, the one-to-one relationship generates one reference in a PDM, with the dominant entity as the parent table. If you do not define a dominant direction, the one-to-one relationship generates two references. In the following example, the author is the dominant entity: 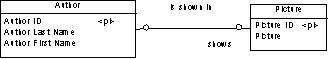 In a PDM, this relationship generates a reference with Author as the parent table, and its primary key migrated to the Picture table as a foreign key: 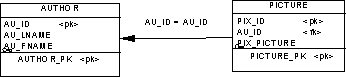 |
For information about the termination points of the relationships in each of the supported notations, see Supported CDM/LDM Notations.
In addition, this tab contains a groupbox for each direction of the relationship, containing the following properties:
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Role name |
Text that describes the relationship of EntityA to EntityB, and which is used to generate the assertion statements displayed at the top of this tab. You should use the infinitive phrase that describes the relationship of one entity to the other. For example, Each Order may contain one or more line., and Each line must belong to one and only one Order. To modify the sentences generated from your role names, edit your model's assertion template (see Assertion Template). |
|
Dependent |
Specifies that the entity is dependent on and partially identified by the other entity. In the following example, the task entity is dependent on the project entity. Each task is a part of a project and each project can contain zero or more tasks: 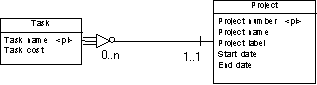 |
|
Mandatory |
Specifies that each instance of the entity requires at least one instance of the other entity. For example, the subcontract relationship is optional from customer to project, but mandatory from project to customer. Each project must have a customer, but each customer does not have to have a project. Implied by dependent |
|
Cardinality |
Specifies the maximum and minimum number of instances of EntityA in relation to EntityB (if mandatory, at least 1). You can choose from the following values: |