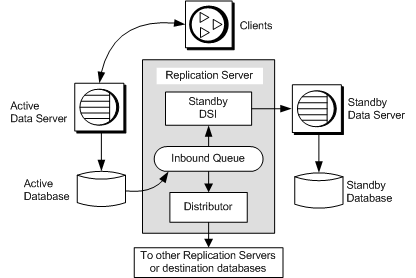
A warm standby application maintains a pair of databases from the same vendor, one of which functions as a standby copy of the other.
Client applications generally update the active database, while Replication Server maintains the standby database as a copy of the active database. Replication Server keeps the standby database consistent with the active database by replicating transactions retrieved from the active database transaction log.
If the active database fails, or if you need to perform maintenance on the active database or data server, you can switch to the standby database so that client applications can resume work with little interruption.
The two databases in a warm standby application appear as a single logical database in the replication system. Depending on your application, this logical database may not participate in replication, or it may be a primary database or a replicate database with respect to other databases in the replication system.
Several Replication Server and Replication Agent features explicitly support warm standby applications. See the Replication Server Administration Guide Volume 2 for more detailed information about warm standby applications.