In a replication system that has one primary Replication Server and many replicate Replication Servers, you can use indirect routes to reduce the load on the primary Replication Server. Indirect routes allow Replication Server to send messages to multiple destinations through a single intermediate Replication Server.
-
Reduced WAN volume
Replication Server distributes one copy of a message to each intermediate site. Replication Servers at the intermediate sites duplicate the messages for each of their outgoing queues.
-
Reduced Replication Server load
Additional Replication Servers running on separate computers share the processing load, reducing the amount of processing required of Replication Servers at primary sites.
-
Fault tolerance
Messages stored at intermediate sites can be used to recover from partition failures at remote sites. See the Replication Server Administration Guide Volume 1 for details.
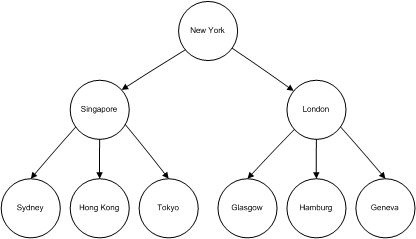
This figure shows how message distribution is handled using intermediate sites. The message follows a direct route to the intermediate sites. From the intermediate site, it follows a direct route to the local site. With this routing arrangement, the primary site sends two messages rather than eight.
Intermediate sites reduce primary site message volume, but they increase the time between updates at the primary and replicate servers. Plan your routes carefully; use only the number of intermediate sites required.
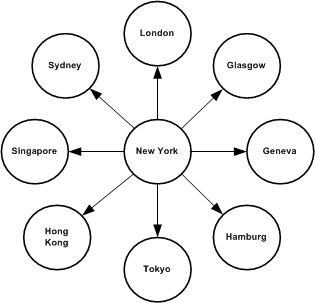
If you do not use intermediate sites, routes are set up in a star configuration.
When a row is updated at a primary site, the primary Replication Server sends messages through the WAN to each remote site that has a subscription for the row. For example, in the above figure, New York can send identical data through eight different routes. If there are many sites, the network is quickly overloaded with redundant messages.
Creating routes in a hierarchical arrangement allows load balancing by reducing the number of connections and messages distributed from the primary site. Additional Replication Servers running on separate computers share the processing load, reducing the amount of processing required of Replication Servers at primary sites.