An XML model (XSM) helps you analyze an XML Schema Definition (.XSD), Document Type Definition (.DTD) or XML-Data Reduced (.XDR) file. You can model, reverse-engineer, and generate each of these file formats.
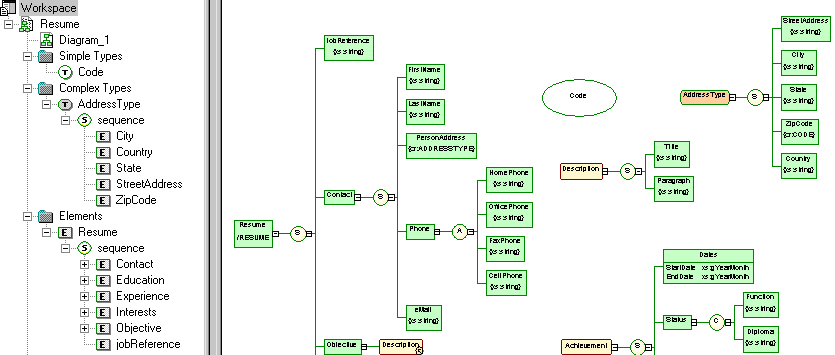
Since XML structures can be very complex, it can be easier to visualize them through diagrams. With its Browser tree view and diagram, an SAP® Sybase® PowerDesigner® XSM gives you a global and schematic view of all the elements composing your XSD, DTD, or XDR:
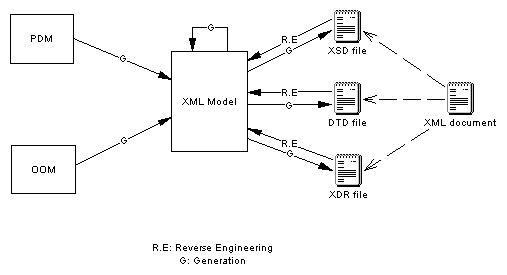
A PowerDesigner XSM allows you to generate and reverse engineer XSD, DTD and XDR files and also generate an XML model from a Physical Data Model (PDM), Object Oriented Model (OOM), or another XSM:
DTD, XSD or XDR
The structure of an XSM is described by a DTD, an XSD or an XDR file:
-
A DTD file is a basic way to describe the structure of an XML document. It is a raw list of all the legal elements making up an XML document. An extract of a DTD file follows:
-
An XSD file (or schema) is an elaborated way to describe the structure of an XML document. It can support namespaces, derivations, keys, simple and complex user-defined data types and a robust collection of predefined data types. An extract of an XSD file follows:
An XSD file always starts with the <schema> tag (root element). All objects created in the model will appear in the XSD file between the schema start-tag and end-tag
-
An XDR file is a simplified XSD file (or schema). It does not support simple and complex user-defined data types. An extract of an XDR file follows:
An XDR file always starts with the <schema> tag (root element). All objects created in the model will appear in the XDR file between the schema start-tag and end-tag
Suggested Bibliography
-
W3C XML Recommendation – http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml
-
W3C DTD Recommendation – http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml#dt-doctype
-
W3C XML Schema Recommendation – http://www.w3.org/XML/Schema#dev
-
W3C XML-Data Note – http://www.w3.org/TR/1998/NOTE-XML-data-0105/