Data Flow - Complex Table
The complex table definition defines a table of records containing multiple fields stored on the SAP Client in a structured and searchable format. A complex table can contain large amounts of data with records numbering in the thousands. Included in the complex table are the fields for its records and indexes on fields to provide search functionality and structure to the overall data in the table. The complex table definition also defines how its data is synchronized.
The following diagram and steps depict what happens when the Agentry Client must load or reload a complex table.
Data Flow - Complex Table
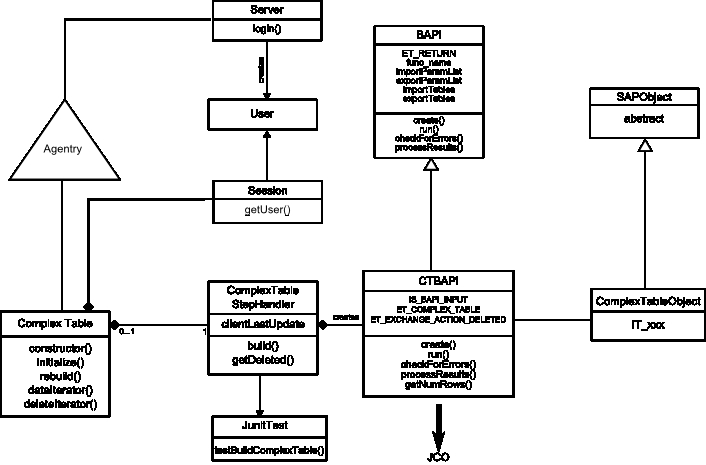

- The complex table's initialize() method is called.
- The initialize() method calls a ComplexTableStepHandler build() static method passing the User object.
- The ComplexTableStepHandler build() method constructs the necessary CTBAPI class, passing the User object and clientLastUpdate parameter to it.
- The CTBAPI constructor retrieves the JCo function object from the repository, using the connection on User.
- CTBAPI sets BAPI import parameter IS_BAPI_INPUT.
- CTBAPI adds IT_xxx record(s) to ComplexTableObject import tables for search criteria or other input parameters.
- ComplexTableStepHandler build() method calls getNumRows() method in CTBAPI.
- CTBAPI getNumRows() method calls the execute() function and checks for exceptions.
- CTBAPI getNumRows() method reads ET_RETURN table in the BAPI class for error messages.
- CTBAPI getNumRows() method iterates over ET_COMPLEX_TABLE and reads records from the table.
- For each record, CTBAPI getNumRows() method calls the appropriate constructor in the appropriate SAPObject subtype.
- The SAPObject subtype constructor maps the JCo record column names to field names.
- CTBAPI getNumRows() method collects the SAPObjects in ComplexTableIterator and passes them back to ComplexTableStepHandler.
- ET_EXCHANGE_ACTION_DELETED is read and follows the same steps as 10 - 13. These SAPObjects populate another ComplexTableIterator.
- ComplexTableHandler passes the iterators back to ComplexTable dataIterator() and deleteIterator().
- ComplexTable initialize() stores the iterators in ComplextTableIterator and returns them to Agentry in dataIterator() and deleteIterator.
- Agentry application defined in the SAP Mobile Server parses these iterators and sends table rows up to Client.
Parent topic: Data Flow