Describes the cache database cache process flow, and options available for diagnosing problems at each step of the process.
Process flow
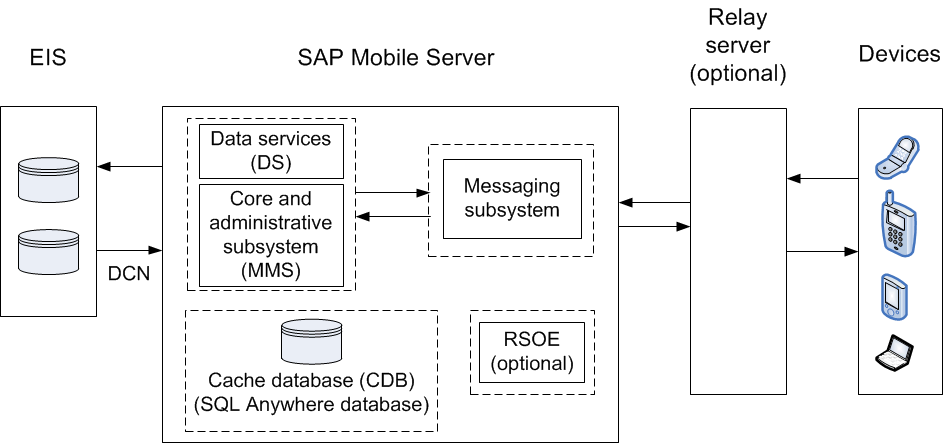
This diagram shows a logical view of the cache process flow on SAP Mobile Platform.
The cache refresh process is either scheduled (repeated at certain intervals) or on-demand when the client initiates a request. The cache can also be updated by incoming Data Change Notification (DCN) requests. A mobile business object (MBO) operation marked as an Invalidate the cache operation forces cache contents to be refreshed.
Troubleshooting options
This section describes the options available for diagnosing cache database cache processing flow problems.
- In SAP Control Center, enable data services (DS) subsystem logging by setting its log level. The output is written in the server log.
- Review subsystem messages for information about getting data and sending transactions.
- For cache activities, you can enable domain logging on the package using SAP Control Center, and then review data in cache sub-systems (Cache Refresh and DS Interface specifically) for the period domain logging is enabled. See Domain Logs and Domain Log Categories related documentation in System Administration and SAP Control Center for SAP Mobile Platform online help for complete details.
In SAP Control Center, check cache group properties such as schedule, and cache interval. Cache updates are propagated to the client based on a combination of settings for Synchronization group change detection interval, push related device settings (messaging synchronization), and notification threshold for subscriptions (replication synchronization). You can view all those properties in the SAP Control Center .
- If you like to troubleshoot at the system-level (which will record all domains and packages activities), you can enable MMS logging by setting the log level in SAP Control Center. The output is written in the server log.
- Select the desired application package, and enable domain logging on that package. Review the captured log messages in SAP Control Center.
- For quick troubleshooting to locate system errors, you can check the package-level client log and MBO/Operation history in the SAP Control Center.
- View the MBO/Operation history in SAP Control Center for errors during back-end interaction with the EIS.
- On
the data-tier node, review the database error logs:
- errorlog.txt – database system errors
- clusterdb_errorlog.txt – cluster DB server log
- monitordb_errorlog.txt – monitor and domainlog DB server log