Understand how to effectively use shared read MBOs.
 |
"Shared-read MBO" refers to MBOs that have caches that are populated by a shared read operation. See Populating the Cache Via a Shared Read Operation. |
 |
All MBOs sharing the common read also share the same partition key—in other words, they are always loaded and refreshed together. See Updating Shared Read MBOs. |
 |
Use shared read whenever possible to increase load efficiency. |
 |
Use multiple partitions, if possible, to alleviate the cost of "Invalidate the cache," as only the affected partition needs to be refreshed. |
 |
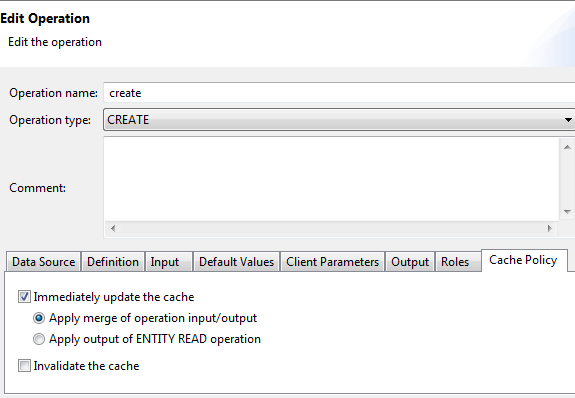
Always enable "Immediately update the cache" for a create operation to maintain surrogate key to (just returned) business key association. |
 |
Use the "Immediately update the cache" cache policy to update an MBO object graph. |
Updating Shared Read MBOs
Use the "Immediately update the cache" operation cache policy and either the "Apply output of ENTITY READ operation" or the "Apply merge of operation input/output" option to transactionally update MBOs in an object hierarchy.
- The remote operation cannot return all the attributes of a composite graph (MBOs in a composite relationship). If the remote operation can return all the attributes, "Apply merge of operation input/output" provides better performance than "Apply output of ENTITY READ operation."
- Using stored procedures, since the MBO developer can use the Entity Read operation without needing to modify any existing stored procedure to get the results into the cache.
Addressing Inconsistency
If it is not always possible to apply results to the CDB for all shared read MBOs in an object hierarchy, the developer must decide whether the temporary inconsistency is an issue for the user. Regardless of whether the CDB needs to be invalidated to force a refresh, the create operation's cache policy should always enable "Immediately update the cache" to allow the CDB to associate the returned business key with the surrogate key from the device. This allows the CDB to avoid deleting the new object on the device in preparation for a new one from the EIS.