This diagram illustrates DCN data flow.
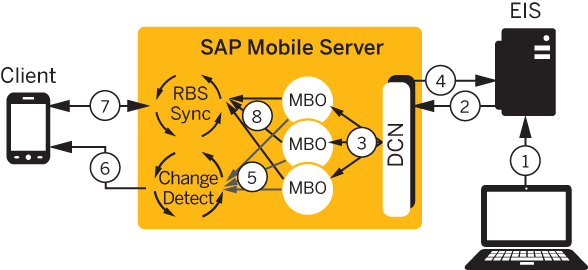
Steps one through four describe DCN, while steps five through eight provide an example of how the change itself is synchronized with the client using targeted change notification (TCN), previously called server-initiated synchronization (SIS), with a client using synchronization parameters.
- EIS update – a program or some other process updates data in the EIS which is associated with a DCN.
- HTTP(S) push – the EIS pushes a DCN message with new or changed MBO data contained in the message on the configured HTTP(S) port.
- DCN operation – the DCN service receives the message and performs the upsert/update to the CDB tables of the corresponding MBOs. DCN upsert/delete operations also set the changed flag of an MBO package to true.
- SAP Mobile Server response – SAP Mobile Server sends a response message back to the EIS that contains the status of each DCN in the submitted message.
- Change detection – for a particular device that needs the new data, SAP Mobile Server generates a message for the client indicating that it should synchronize.
- Change notification – the message is pushed from
SAP Mobile Server to the device.The flow assumes that the device is registered for notifications and comes online to receive the notification:
- If the device is online (as viewed in SAP Control Center, Application Connections), then the notification message is immediately delivered to the device and the application handles the notification accordingly (the developer must code for this scenario).
- If the device is offline, then the notification is queued and the "Pending Count" for that application connection increases and can be observed to be non-zero in the same SAP Control Center screen (Application Connections). Optionally, for iOS, APNS can be configured to provide notification to the device/application which ultimately results in the user launching the application, causing it to reconnect to SAP Mobile Server to retrieve the notification.
- RBS synchronization – the client receives the message and issues a synchronization request to SAP Mobile Server.
- Synchronization – SAP Mobile Server retrieves the new/updated data based on the client synchronization parameter and returns it to the client.