Replication-based synchronization (RBS) data flow for regular DCN differs slightly from message-based synchronization (MBS).
RBS DCN data flow:
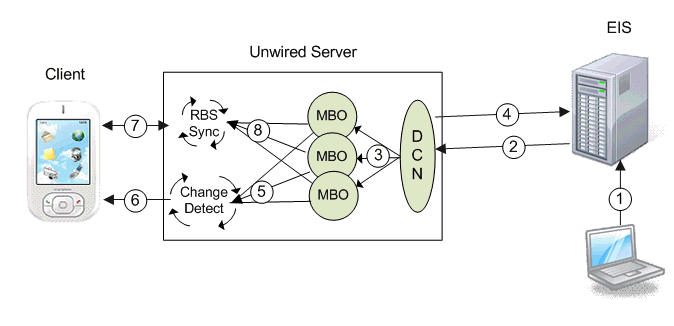
- EIS update – a program or some other process updates data in the EIS which is associated with a DCN.
- HTTP(S) push – the EIS pushes a DCN message with new or changed MBO data contained in the message on the configured HTTP(S) port.
- DCN operation – the DCN service receives the message and implements the upsert/update function into the CDB tables of the corresponding MBOs. DCN upsert/delete operations also sets the changed flag of an MBO package to true.
- Unwired Server response – Unwired Server sends a response message back to the EIS that contains the status of each DCN in the submitted message.
- Change detection – for a particular device that returns new data, Unwired Server generates a message for the client indicating that it should synchronize.
- Change notification – the message is pushed from Unwired Server to the device.
- RBS synchronization – the client receives the message and issues a synchronization request to Unwired Server.
- Synchronization – Unwired Server retrieves the new/updated data based on the client synchronization parameter and returns it to the client.
MBS DCN data flow:
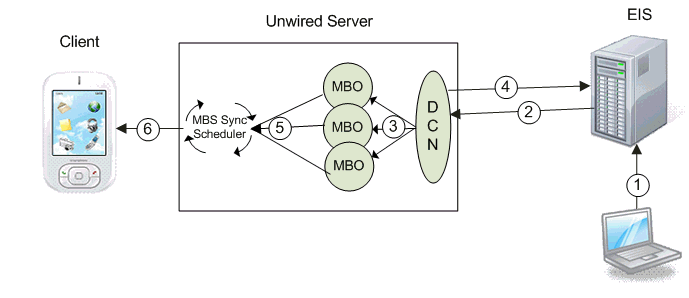

- EIS update – a program or some other process updates data in the EIS which is associated with a DCN.
- HTTP(S) push – the EIS pushes a DCN message with new or changed MBO data contained in the message on the configured HTTP(S) port.
- DCN operation – (with payload) the DCN service receives the message and implements the upsert/update function into the CDB tables of the corresponding MBOs. DCN upsert/delete operations also sets the changed flag of an MBO package to true.
- Unwired Server response – Unwired Server sends a response message back to the EIS that contains the status of each DCN in the submitted message.
- synchronization triggered – Unwired Server checks the changed flag status for the package when the synchronization group schedule time is reached. If the flag is true, Unwired Server retrieves a list of all subscribed devices for this package and synchronizes. If synchronization logic for a particular device returns new data, an MBS message is generated for that device.
- MBS push – the MBS message is pushed from Unwired Server to the device.
When the client receives this message, it performs the corresponding create, update, or delete operation on the device's mobile database.