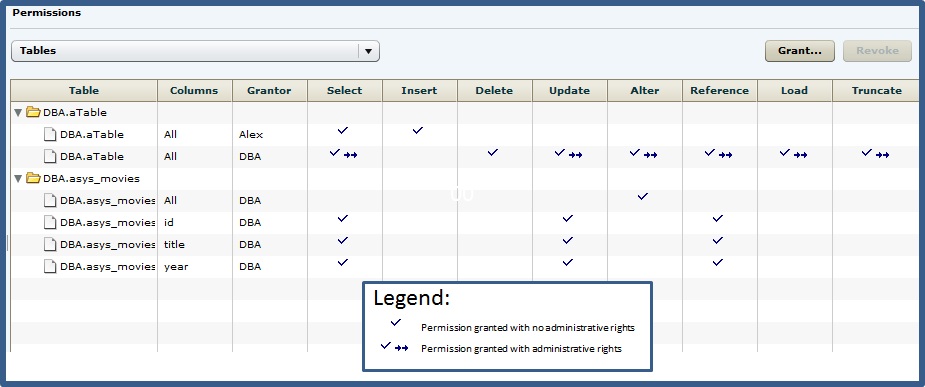
The Tables permissions list displays permission details the tables and column directly granted to a user, user-extended role, or standalone role
- SELECT – table or column level
- INSERT – table level only
- DELETE – table level only
- UPDATE – table or column level
- ALTER – table level only
- REFERENCE – table or column level
- LOAD – table level only
- TRUNCATE – table level only
- You own the object.
- You are granted the MANAGE ANY OBJECT PRIVILEGE system privilege.
- You have been indirectly granted specific permissions through membership in a role to which permissions have been directly or indirectly granted.
- You have been directly granted specific permissions.
Users or roles with object ownership or the MANAGE ANY OBJECT PRIVILEGE system privilege are automatically granted all possible object permissions with administrative rights.
Object permissions can be granted with or without administrative rights. When granted without administrative rights, the grantee can perform authorized tasks requiring the permission, but cannot in turn grant the permission to another user or role. When granted with administrative rights (With grant option), the grantee can do both.
The permissions list only lists those tables or columns object permissions granted directly to the selected user or role. The list indicates the table and column the permission is granted on, by who (grantor), and the permissions and their corresponding administrative rights. The permissions list does not list object permissions obtained through ownership, the MANAGE ANY OBJECT PRIVILEGE system privilege, or role membership.
For each table, permissions granted to all columns on the table are listed first (all), followed by each column, sorted alphabetically by column name.
When granted to a role, permissions, including administrative rights, are inherited by all members of the role. The role, not the users indirectly granted the permissions through inheritance, appear on the permissions list.
The REVOKE command applies to the database object permission itself, not to any administrative right granted on the permission. Therefore, to remove the administrative right only and leave the database object permission intact, do not use the Revoke button. Rather, regrant the specific permission without administrative rights. Only the original grantor can remove the administrative rights only from a granted permission. If another grantor regrants the same permission without administrative rights, a new permission without administrative rights is granted, but the original permission with administrative rights remains and takes precedence over any other non-administrative grants of the same permission to the same user or role.
If multiple permissions are granted, you can revoke some or all of the permissions. However, if you revoke a permission granted administrative rights, and the grantee has granted the permission to other users, who in turn have granted it to other users, and so on, every grantee in the chain who has received the permission indirectly, with or without administrative rights, also has their permission revoked. For example, UserA is granted the SELECT permission with the With grant option. UserA grants SELECT to UserB with the With grant option. UserB grants SELECT to UserC and UserD without administrative rights and to UserE with administrative rights. When you revoke the SELECT permission from UserA, it is also revoked for UserB, UserC, UserD and UserE.
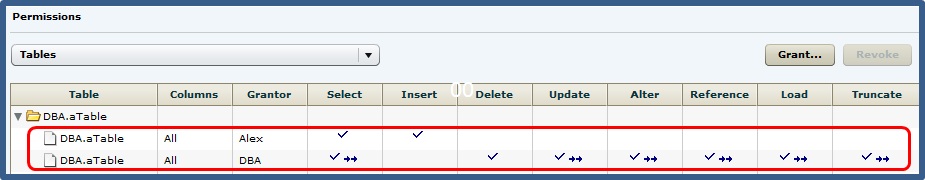
Permissions can be granted on the same table or column, by multiple grantors, resulting in the same table or column appearing multiple times on the list. If the same permission is granted to the same table or column, with and without administrative rights, the grant with the administrative right takes precedence.
In this example, the user is granted the SELECT permission by both DBA and Alex, with different administrative rights. When the same permission is granted with different administrative rights, the higher administrative right takes precedence.
When revoking a permission granted multiple times, the permission is revoked from all instances, regardless of administrative rights. For example, Manager1 grants User2 INSERT with administrative rights. User1 also grants INSERT to User2, but without administrative rights. Regardless of which instance of INSERT is revoked, both instances of INSERT are revoked for User2.