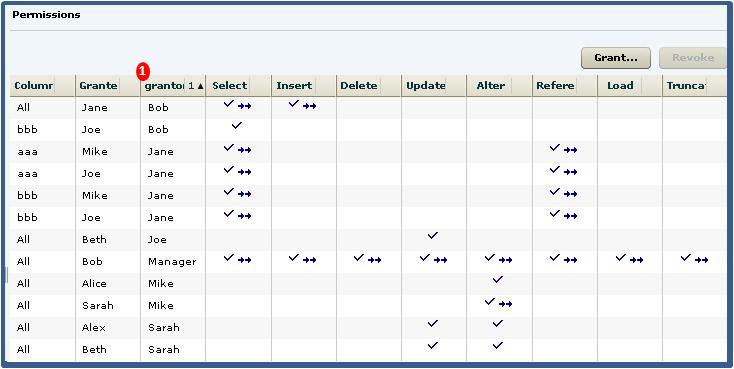
Before revoking a grantee's permission, you need to identify grantees directly or indirectly granted the permission from the original grantee.
The grant chain traces how a grantee has in turn granted a permission to other grantees.
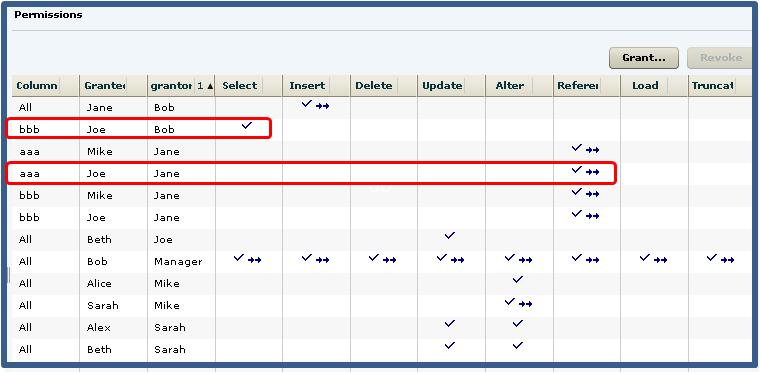
- Bob is granted all permissions with administrative rights to all columns in the table.
- Bob grants Joe SELECT permission without administrative rights to column bbb only. Bob also grants Jane SELECT and INSERT permissions with administrative rights to all columns.
- Jane grants Mike and Joe SELECT and REFERENCE permissions with
administrative rights to columns aaa and bbb. Jane also grants Beth and Mary
UPDATE permissions without administrative rights on column ccc.Note: Joe has now been granted the SELECT permission twice, with different administrative rights, by different grantors, to different columns.
- Joe grants Beth UPDATE permission without administrative rights to all
columns in the table.Note: Beth has now been granted the UPDATE permission twice, by different grantors, at both the column and table level.
- Mike grants Sarah ALTER permission with administrative rights to all columns in the table. Mike also grants Alice ALTER permission without administrative rights, again to the whole table.
- Sarah grants Alex and Beth ALTER and UPDATE permissions without
administrative rights on all columns.Note: Beth has now been granted the ALTER permission multiple times, by different grantors, on different columns.
The permissions list would appear similar to:
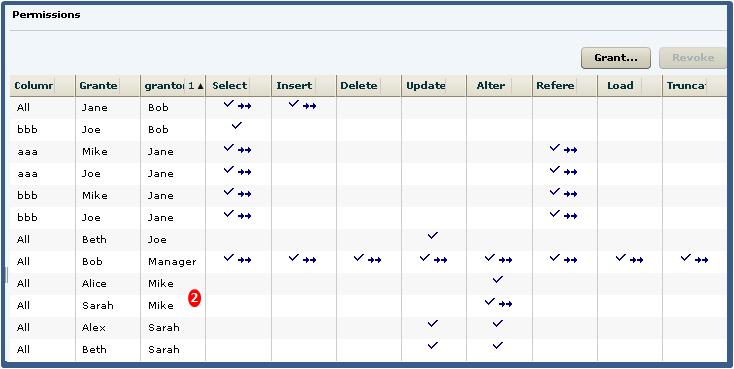
- Sort the list by Grantor and locate all instances of administrative grants
of SELECT by Jane.Note: There are four instances of Jane granting permissions. Since we are revoking the SELECT permission only, only those grants involving the SELECT permission will be impacted. Therefore, revoking Jane's SELECT permission will also revoke the permission from Mike and Joe, on columns aaa and bbb. Of the SELECT permissions, you only need to follow those involving administrative rights.
- Locate Mike in the Grantor column. Note: Mike granted ALTER to Sarah and Alice. Both were granted the SELECT permission as an indirect (once removed) result of Jane. It does not matter whether the grant included administrative rights. Therefore, their SELECT permission will also be revoked when Jane's is revoked. Since Alice was granted SELECT without administrative rights, her grant chain ends. Since Sarah was granted SELECT with administrative rights, her grant chain continues.
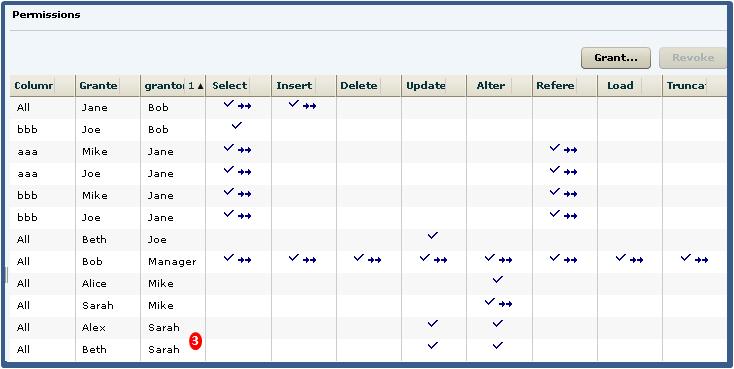
- Locate Sarah in the Grantor column.Note: Sarah granted ALTER and UPDATE to Beth and Alex. Both were granted the SELECT permission as an indirect (twice removed) result of Jane. Again, administrative rights do not matter, and since neither grant was with administrative rights, the grant chain ends.
To summarize, revoking Jane's SELECT permission revokes the permission from Mike,
Joe, Beth, and Mary, through direct granting or permissions by Jane, but also
revokes the permission from Alice, Sarah, Alex, and Role1 as a result of indirect
from Jane. The permissions list after revoking Jane's SELECT permission would appear
similar to:
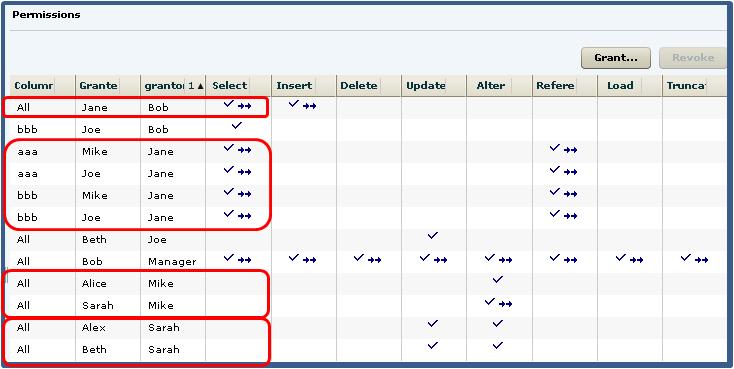
It is important to note that it is possible for a user
to retain an "identified" permission after revoke it the same permission was granted
by multiple grantors. In this scenario, both Bob and Jane granted the SELECT
permission to Joe, so Joe retains the SELECT permission granted by Bob. If a grantee
has been granted multiple permissions, only those permissions explicitly selected
are revoked. In this scenario, only the SELECT permission was revoked from Joe. The
REFERENCE permission remains granted, even though it was also granted by Jane.