Minor changes in your environment can solve some network performance issues.
Improving Large Data Transfers
Perform large transfers during off-hour periods, if possible.
Limit the number of concurrent queries during large transfers.
Do not run queries and insertions concurrently during large transfers.
Use stored procedures to reduce total traffic.
Use row buffering to move large batches through the network.
- If large transfers are common, consider installing better network hardware that is suitable for such transfers. For example:
Token ring–responds better during heavy utilization periods than ethernet hardware.
Fiber optic–provides very high bandwidth, but is usually too expensive to use throughout the entire network.
Separate network–can be used to handle network traffic between the highest volume workstations and the server.
Isolate Heavy Network Users
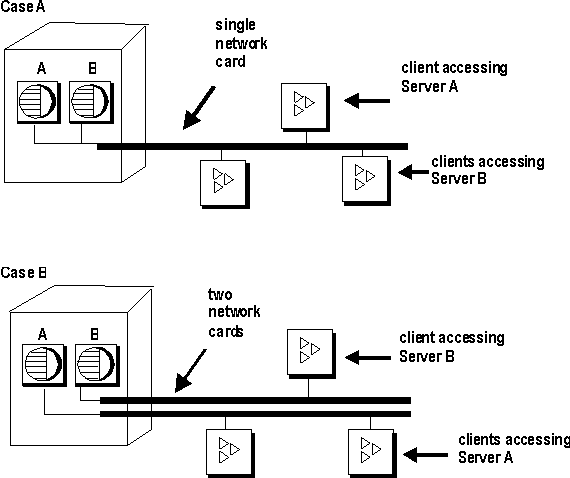
In case A in Figure 12-4, clients accessing two different database servers use one network card. That means that clients accessing Servers A and B have to compete over the network and past the network card. In the case B, clients accessing Server A use a different network card than clients accessing Server B.
It would be even better to put your database servers on different machines. You may also want to put heavy users of different databases on different machines.
Put Small Amounts of Data in Small Packets
If you send small amounts of data over the network, keep the default network packet size small (default is 512 bytes). The -p server start-up option lets you specify a maximum packet size. Your client application may also let you set the packet size.