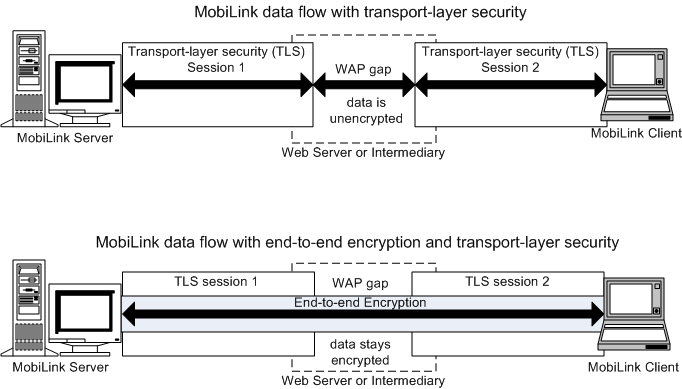
End-to-end encryption occurs when data is encrypted at the point of origin and decrypted at the final destination. There is no point during transmission that the data is unencrypted.
MobiLink TLS is sometimes only used to encrypt data up to an intermediary (for example, encryption/decryption hardware) between the client and server. At the intermediary, the data would be decrypted and then encrypted again by the intermediary for the rest of the journey. Notably, this happens when synchronizing via HTTPS through a Web server. The brief interval when the data is unencrypted in the intermediary is sometimes called the Wireless Application Protocol gap or WAP Gap.
Within a corporation, a WAP gap is often acceptable when the intermediary is within corporate control. However, in a third-party hosted environment where data from different corporations is going through the same WAP gap, sensitive data may be exposed. End-to-end encryption prevents any intermediary from accessing the data because the synchronization stream is encrypted from start to finish, and may optionally be encrypted once more with TLS.
For information about how to enable end-to-end encryption on the MobiLink client, see the following topics:
For information about how to set up end-to-end encryption on the MobiLink server, see the following topics:
 See also
See also |
Discuss this page in DocCommentXchange.
|
Copyright © 2012, iAnywhere Solutions, Inc. - SQL Anywhere 12.0.1 |